Unique circulating microRNA profiles in epidemic Kaposi's sarcoma
- PMID: 35570854
- PMCID: PMC9065625
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2022.02.002
Unique circulating microRNA profiles in epidemic Kaposi's sarcoma
Abstract
Background: Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8) causes Kaposi's sarcoma (KS). Kaposi sarcoma in HIV/AIDS patients is referred to as epidemic KS and is the most common HIV-related malignancy worldwide. The lack of a diagnostic assay to detect latent and early-stage disease has increased disease morbidity and mortality. Serum miRNAs have previously been used as potential biomarkers of normal physiology and disease. In the current study, we profiled unique serum miRNAs in patients with epidemic KS to generate baseline data to aid in developing a miRNA-based noninvasive biomarker assay for epidemic KS.
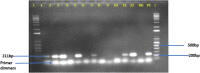
Methods: This was a comparative cross-sectional study involving 27 patients with epidemic KS and 27 HIV-positive adults with no prior diagnosis or clinical manifestation of KS. DNA and RNA were isolated from blood and serum collected from study participants. Nested PCR for circulating HHV-8 DNA was performed on the isolated DNA, whereas miRNA library preparation and sequencing for circulating miRNA were performed on the RNA samples. The miRge2 pipeline and EdgeR were used to analyse the sequencing data.
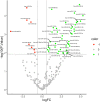
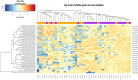
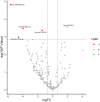
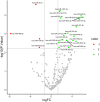
Results: Fifteen out of the 27 epidemic KS-positive subjects (55.6%) tested positive for HHV-8 DNA, whereas only 3 (11.1%) out of the 27 HIV-positive, KS-negative subjects tested positive for HHV-8 DNA. Additionally, we found a unique miRNA expression signature in 49 circulating miRNAs in epidemic KS subjects compared to subjects with no epidemic KS, with 41 miRNAs upregulated and 8 miRNAs downregulated. Subjects with latent KS infection had a differential upregulation of circulating miR-193a compared to HIV-positive, KS-negative subjects for whom circulating HHV-8 DNA was not detected. Further analysis of serum from epidemic KS patients revealed a miRNA signature according to KS tumor status and time since first HIV diagnosis.
Conclusions: This study reveals unique circulating miRNA profiles in the serum of patients with epidemic KS versus HIV-infected subjects with no KS, as well as in subjects with latent KS. Many of the dysregulated miRNAs in epidemic KS patients were previously reported to have crucial roles in KS infection and latency, highlighting their promising roles as potential biomarkers of latent or active KS infection.
Keywords: Biomarker; Blood; Circulating microRNA; Kaposi's sarcoma; Serum; microRNA.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

