Prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor desidustat improves anemia in erythropoietin hyporesponsive state
- PMID: 35570856
- PMCID: PMC9096675
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100102
Prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor desidustat improves anemia in erythropoietin hyporesponsive state
Abstract
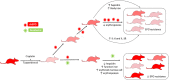
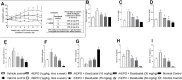
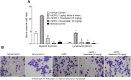
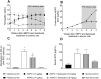
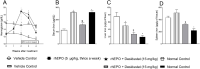
Many anemic chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients are refractory to erythropoietin (EPO) effects due to inflammation, deranged iron utilization, and generation of EPO antibodies. This work assessed the effect of desidustat, an inhibitor of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) prolyl hydroxylase (PHD), on EPO-refractory renal anemia. Sprague Dawley rats were made anemic by cisplatin (5 mg/kg, IP, single dose) and turpentine oil (5 mL/kg, SC, once a week). These rats were given recombinant human EPO (rhEPO, 1 μg/kg) and desidustat (15 or 30 mg/kg) for eight weeks. Separately, rhEPO (1-5 μg/kg) was given to anemic rats to sustain the normal hemoglobin levels and desidustat (15 mg/kg) for eight weeks. In another experiment, the anemic rats were treated rhEPO (5 μg/kg) for two weeks and then desidustat (15 mg/kg) for the next two weeks. Dosing of rhEPO was thrice a week, and for desidustat, it was on alternate days. Desidustat inhibited EPO-resistance caused by rhEPO treatment, decreased hepcidin, IL-6, IL-1β, and increased iron and liver ferroportin. Desidustat reduced EPO requirement and anti-EPO antibodies. Desidustat also maintained normal hemoglobin levels after cessation of rhEPO treatment. Thus, novel prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor desidustat can treat EPO resistance via improved iron utilization and decreased inflammation.
Keywords: Antibody; Desidustat; EPO resistance; Inflammation.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Desidustat: a novel PHD inhibitor for the treatment of CKD-induced anemia.Front Nephrol. 2024 Oct 22;4:1459425. doi: 10.3389/fneph.2024.1459425. eCollection 2024. Front Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39502472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological inhibition of prolyl hydroxylase protects against inflammation-induced anemia via efficient erythropoiesis and hepcidin downregulation.Eur J Pharmacol. 2019 Jan 15;843:113-120. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.11.023. Epub 2018 Nov 17. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30458168
-
Prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor desidustat protects against acute and chronic kidney injury by reducing inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress.Drug Dev Res. 2021 Sep;82(6):852-860. doi: 10.1002/ddr.21792. Epub 2021 Jan 22. Drug Dev Res. 2021. PMID: 33480036
-
Balancing Efficacy, Health Status, and Cost-Effectiveness: A Comparative Study of Desidustat and Erythropoietin in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients on Hemodialysis.G Ital Nefrol. 2025 Feb 28;42(1):2025-vol1. doi: 10.69097/42-01-2025-09. G Ital Nefrol. 2025. PMID: 40026228 Clinical Trial.
-
Desidustat: First Approval.Drugs. 2022 Jul;82(11):1207-1212. doi: 10.1007/s40265-022-01744-w. Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35834123 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Desidustat: a novel PHD inhibitor for the treatment of CKD-induced anemia.Front Nephrol. 2024 Oct 22;4:1459425. doi: 10.3389/fneph.2024.1459425. eCollection 2024. Front Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39502472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renal anemia: from relative insufficiency of EPO to imbalance of erythropoiesis and eryptosis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2024 Nov;56(11):3559-3568. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04146-x. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Int Urol Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38982020 Review.
-
Progress in the application of novel inflammatory indicators in chronic kidney disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jan 30;12:1500166. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1500166. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39950124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio for the clinical outcomes of chronic kidney diseases: an update systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Jul 28;26(1):419. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04363-1. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40721748 Free PMC article.
-
A Case of Erythropoietin (EPO)-Induced Pure Red Cell Aplasia and Its Treatment Efficacy With Desidustat.Cureus. 2024 Jun 9;16(6):e62022. doi: 10.7759/cureus.62022. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38989377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beck J., Henschel C., Chou J., Lin A., Del Balzo U. Evaluation of the carcinogenic potential of roxadustat (FG-4592), a small molecule inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase in CD-1 mice and Sprague Dawley rats. Int. J. Toxicol. 2017;36(6):427–439. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

