Student-Driven Course-Based Undergraduate Research Experience (CUREs) Projects in Identifying Vaginal Microorganism Species Communities to Promote Scientific Literacy Skills
- PMID: 35570970
- PMCID: PMC9096218
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.870301
Student-Driven Course-Based Undergraduate Research Experience (CUREs) Projects in Identifying Vaginal Microorganism Species Communities to Promote Scientific Literacy Skills
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Student-driven course-based undergraduate research experience (CUREs) projects in identifying vaginal microorganism species communities to promote scientific literacy skills.Front Public Health. 2025 Apr 4;13:1576281. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1576281. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40255383 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objectives: We aim to build a students' own engagement in original microbiological course-based undergraduate research experience (CUREs) model served two research and teaching scientific purposes including students' scientific literacy skills and instructors' role, which could further be applied as contribution to broader scientific knowledge and conduct novel research in their future research experience and careers.
Methods: We describe a student-driven CUREs model on the microorganism species in female vaginal using general bacterial culture techniques and high-throughput 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing to enable students to center experimental research method under the direction of instructors. A total of 8 undergraduate students and 5 instructors from Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine participated in the project. The CUREs were divided in four operating scopes: project planning, implementation, summarizing and feedback phases. Instructors help students to develop learning research goals.
Results: This project helped students to gain "hard skills" experiences in scientific theoretical research process and technical practices. Students reached the conclusion that Lactobacillus species dominated the primary vaginal microbiota in reproductive-age women, 16S rRNA sequencing is a method widely applied for microbiology detection. CUREs also increased students' engagement in scientific experiments and promote 3 learning goals in "soft skills": (1) Develop students' self-study and efficacy ability, expression capability and professional research communication skills; (2) Strengthen students' motivation and ownership in science research, overcoming failure, benefitting persistence and patience, building professional science identity, competence, and confidence in collaboration, implement spirit of rigorous and carefulness; (3) Obtain authorship, independent and logical thinking capability, summarizing ability and confidence enhancement. Instructors proposed guiding research question for the students and determine evidence in achieving pedagogical goals in CUREs.
Conclusions: Our microbiological CUREs project served two scientific purposes: research and teaching, which increase students' engagement in promoting learning gains in scientific research skills, ownership, identity development, and spirit of motivation, self-efficacy, persistence, collaboration, communication, as well as opportunities to make relevant scientific discoveries. These abilities equipped them with essential foundation for the subsequent collaborative experiments and future scientific study.
Keywords: 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing; course-based undergraduate research experiences; scientific literacy skills; student-driven; vaginal microorganisms.
Copyright © 2022 Yang, Wang, Sang, Zhang, Liu and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



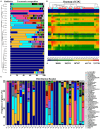
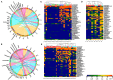
References
-
- Olimpo J. Disease and the environment: a health disparities CURE incorporating civic engagement education. Sci Educ Civic Engag. (2019) 11:13–24. Available online at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/332652829
-
- Corwin LA, Runyon CR, Eman G, Moriah S, Greg C, Palmer GC, et al. . Effects of discovery, iteration, and collaboration in laboratory courses on undergraduates' research career intentions fully mediated by student ownership. Cbe Life Sci Educ. (2018) 17:ar20. 10.1187/cbe.17-07-0141 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

