Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of VIS649 (Sibeprenlimab), an APRIL-Neutralizing IgG2 Monoclonal Antibody, in Healthy Volunteers
- PMID: 35570983
- PMCID: PMC9091613
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2022.01.1073
Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of VIS649 (Sibeprenlimab), an APRIL-Neutralizing IgG2 Monoclonal Antibody, in Healthy Volunteers
Abstract
Introduction: VIS649 (sibeprenlimab), a humanized IgG2 monoclonal antibody that inhibits APRIL, is being developed as a potential treatment for IgA nephropathy (IgAN). This phase 1, first-in-human, randomized, double-blind, single ascending dose study aimed to evaluate the safety, pharmacokinetics (PK), and pharmacodynamics (PD) of VIS649 in healthy adults.
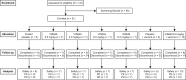
Methods: Participants were randomized to VIS649 (sequential i.v. dosing cohorts: 0.5, 2.0, 6.0, 12.0 mg/kg) or placebo; a further cohort received VIS649 6.0 mg/kg or placebo followed by a tetanus/diphtheria vaccine challenge.
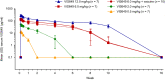
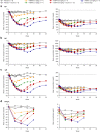
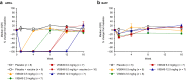
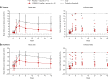
Results: A total of 51 participants were randomized, dosed, and analyzed for safety (7 for each VIS649 dose; 8 for placebo; 10 for VIS649 + vaccine; 5 for placebo + vaccine). There were no serious adverse events (AEs) or AEs leading to study discontinuation. VIS649 had nonlinear PK: half-life increased with dose and drug exposure increased in a greater than dose-proportional manner. Serum APRIL, IgA, galactose-deficient (Gd) IgA1, IgG, and IgM were reversibly suppressed in a dose-dependent manner, with a dose-response in time to recovery. Tetanus and diphtheria serum IgG titers increased after recall vaccination.
Conclusion: VIS649 was safe, well tolerated, and reversibly suppressed APRIL and various immunoglobulins, without loss of antigen-specific vaccination response. Further clinical development of VIS649 for IgAN is warranted. Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT03719443.
Keywords: APRIL; IgA nephropathy; clinical trial; galactose-deficient IgA; glomerulonephritis; monoclonal antibody.
© 2022 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

