High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents: Current Perspectives and Strategies to Improve Future Kidney and Cardiovascular Health
- PMID: 35570999
- PMCID: PMC9091586
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2022.02.018
High Blood Pressure in Children and Adolescents: Current Perspectives and Strategies to Improve Future Kidney and Cardiovascular Health
Abstract
Hypertension is one of the most common causes of preventable death worldwide. The prevalence of pediatric hypertension has increased significantly in recent decades. The cause of this is likely multifactorial, related to increasing childhood obesity, high dietary sodium intake, sedentary lifestyles, perinatal factors, familial aggregation, socioeconomic factors, and ethnic blood pressure (BP) differences. Pediatric hypertension represents a major public health threat. Uncontrolled pediatric hypertension is associated with subclinical cardiovascular disease and adult-onset hypertension. In children with chronic kidney disease (CKD), hypertension is also a strong risk factor for progression to kidney failure. Despite these risks, current rates of pediatric BP screening, hypertension detection, treatment, and control remain suboptimal. Contributing to these shortcomings are the challenges of accurately measuring pediatric BP, limited access to validated pediatric equipment and hypertension specialists, complex interpretation of pediatric BP measurements, problematic normative BP data, and conflicting society guidelines for pediatric hypertension. To date, limited pediatric hypertension research has been conducted to help address these challenges. However, there are several promising signs in the field of pediatric hypertension. There is greater attention being drawn on the cardiovascular risks of pediatric hypertension, more emphasis on the need for childhood BP screening and management, new public health initiatives being implemented, and increasing research interest and funding. This article summarizes what is currently known about pediatric hypertension, the existing knowledge-practice gaps, and ongoing research aimed at improving future kidney and cardiovascular health.
Keywords: blood pressure; cardiovascular health; children; hypertension; kidney disease; pediatric.
© 2022 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
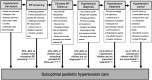
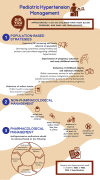
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

