Coronavirus disease: Dental review
- PMID: 35571302
- PMCID: PMC9106232
- DOI: 10.4103/jomfp.jomfp_288_21
Coronavirus disease: Dental review
Abstract
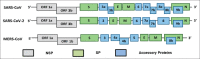
COVID-19 was declared a pandemic outbreak by the World Health Organization, creating a significant impact on health care system. Realizing the high risk associated with this disease and its high rate of transmission, dentists were instructed by health authorities, to stop providing treatment which includes aerosols and droplets and only except emergency complaints. This was mainly for protection of dental healthcare personnel, their families, contacts, and their patients from the transmission of virus. Hence, this review focuses on the life cycle of COVID-19, its clinical symptoms and several issues concerned directly to dental practice in terms of prevention, treatment, and orofacial clinical manifestations.
Keywords: Coronavirus disease-2019; SARS-CoV-2; dental aspect.
Copyright: © 2022 Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Organization WH. Laboratory Testing of Human Suspected Cases of Novel Coron- avirus (nCoV) Infection: Interim Guidance. World Health Organization; 2020. [Last accessed on 2022 Jan 30]. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/330374 .
-
- Gorbalenya AE, Baker SC, Baric RS, de Groot RJ, Drosten C, Gulyaeva AA, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: The species and its viruses – a statement of the Coronavirus Study Group. bioRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.02.07.937862. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous