Targeting the M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 35571495
- PMCID: PMC9069568
- DOI: 10.1042/NS20210004
Targeting the M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
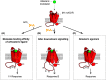
Alzheimer's disease (AD) remains a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, and despite extensive research, only a few drugs are available for management of the disease. One strategy has been to up-regulate cholinergic neurotransmission to improve cognitive function, but this approach has dose-limiting adverse effects. To avoid these adverse effects, new drugs that target specific receptor subtypes of the cholinergic system are needed, and the M1 subtype of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (M1-mAChR) has been shown to be a good target for this approach. By using several strategies, M1-mAChR ligands have been developed and trialled in preclinical animal models and in human studies, with varying degrees of success. This article reviews the different approaches to targeting the M1-mAChR in AD and discusses the advantages and limitations of these strategies. The factors to consider in targeting the M1-mAChR in AD are also discussed.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; acetylcholine; allosteric regulation; muscarinic receptor; orthosteric.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures





References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

