Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for the Detection of Volatile and Off-Odor Compounds in Food Matrices
- PMID: 35571784
- PMCID: PMC9096822
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c07288
Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for the Detection of Volatile and Off-Odor Compounds in Food Matrices
Abstract
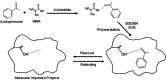
Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) are synthetic receptors having specific cavities intended for a template molecule with a retention mechanism that depends on molecular recognition of the targeted constituent. They were initially established for the detection of minor molecules including drugs, pesticides, or pollutants. One of the most remarkable areas where MIPs have potential utilization is in food analysis, especially in terms of volatile compounds which are found in very low concentrations in foods but play a crucial role for consumer preference and acceptance. In recent years, these polymers have been used extensively for sensing volatile organic and off-odor compounds in terms of food quality for selective high-extraction purposes. This review first summarizes the basic principles and production processes of MIPs. Second, their recent applications in the separation, identification, and quantification of volatile and off-odor compounds in food samples are elucidated.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Huang C.; Wang H.; Ma S.; Bo C.; Ou J.; Gong B. Recent Application of Molecular Imprinting Technique in Food Safety. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1657, 462579.10.1016/j.chroma.2021.462579. - DOI - PubMed
- Villa C. C.; Sánchez L. T.; Valencia G. A.; Ahmed S.; Gutiérrez T. J. Molecularly imprinted polymers for food applications: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 642–669. 10.1016/j.tifs.2021.03.003. - DOI
-
- Leibl N.; Haupt K.; Gonzato C.; Duma L. Molecularly imprinted polymers for chemical sensing: A tutorial review. Chemosensors 2021, 9 (6), 123.10.3390/chemosensors9060123. - DOI
- Jin Y. Z.; Jin Y. Z.; Piao J. Y.; Jin Y. S.; Xuan Y. H. Application and Development of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer to Solid Phase Extraction. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 781–784, 1359–1365. 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.781-784.1359. - DOI
-
- Jin Y.; Xuan Y. H.; Jin Y. S.; Row K. H. Multi-Spe of Caffeine and Catechin Compounds from Green Tea by Caffeine and (+) Catechin MIPS. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2011, 34 (15), 1604–1616. 10.1080/10826076.2011.576296. - DOI
-
- Wullf G.; Sarhan A. The Use of Polymers with Enzyme-Analogous Structures for the Resolution of Racemates. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 1972, 11 (4), 341–344.
-
- Andersson L.; Sellergren B.; Mosbach K. Imprinting of Amino Acid Derivatives in Macroporous Polymers. Tetrahedron Lett. 1984, 25 (45), 5211–5214. 10.1016/S0040-4039(01)81566-5. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

