Hepatocellular Carcinoma: How the Gut Microbiota Contributes to Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapy
- PMID: 35572649
- PMCID: PMC9092458
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.873160
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: How the Gut Microbiota Contributes to Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapy
Abstract
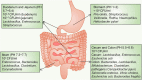
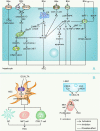
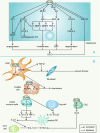
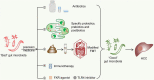
The gut microbiota is gaining increasing attention, and the concept of the "gut-liver axis" is gradually being recognized. Leaky gut resulting from injury and/or inflammation can cause the translocation of flora to the liver. Microbiota-associated metabolites and components mediate the activation of a series of signalling pathways, thereby playing an important role in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). For this reason, targeting the gut microbiota in the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of HCC holds great promise. In this review, we summarize the gut microbiota and the mechanisms by which it mediates HCC development, and the characteristic alterations in the gut microbiota during HCC pathogenesis. Furthermore, we propose several strategies to target the gut microbiota for the prevention and treatment of HCC, including antibiotics, probiotics, faecal microbiota transplantation, and immunotherapy.
Keywords: diagnosis; gut microbiota; gut-liver axis; hepatocellular carcinoma; treatment.
Copyright © 2022 Luo, Guo, Zhou, Zhao, Wang, Sang, Chang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

