Partial upper sternotomy for aortic valve replacement provides similar mid-term outcomes as the full sternotomy
- PMID: 35572904
- PMCID: PMC9096275
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-21-1494
Partial upper sternotomy for aortic valve replacement provides similar mid-term outcomes as the full sternotomy
Abstract
Background: Minimally invasive aortic valve replacement via upper partial sternotomy (MiniAVR) provides very good short-term results and delivers certain advantages in the postoperative course. There is limited data regarding the mid-term mortality and morbidity following this minimally invasive surgery.
Methods: We provide a retrospective analysis of the patients, undergoing MiniAVR versus full sternotomy (FS) for aortic valve replacement with biological prosthesis. As the primary combined end-point the combination of death, stroke, and rehospitalization within 3 years postoperatively was defined. Data have been collected from National Cardiac Surgery Registry and insurance companies.
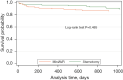
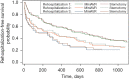
Results: Two hundred consecutive patients with aortic valve replacement (100 ministernotomy in MiniAVR group and 100 full sternotomy in FS group) with biological prosthesis were included in this study. Ministernotomy had longer cross-clamp and bypass times (median difference 6.5 min, P=0.005, and 8.5 min, P=0.002 respectively). Patients operated via upper partial sternotomy had a lower postoperative bleeding [300 mL (IQR, 290) vs. 365 mL (IQR, 207), P=0.031]. There was no difference in the 3-year mortality (14% vs. 11%, P=0.485). The mean number of readmission 3 years after surgery per capita was almost the same in both groups (1.65 vs. 1.60, P=0.836). Median time to the first readmission was longer in the MiniAVR group (difference 8.9 months). The incidence of combined end-point during 3 years postoperatively in both groups was not statistically different (P=0.148), as well as readmissions from cardio-vascular reasons (subhazard ratio 0.90, P=0.693).
Conclusions: Upper partial sternotomy can be performed safely for aortic valve replacement, without increased risk of death, stroke or re-admission in 3 years postoperatively.
Keywords: Minimally invasive; aortic valve; partial sternotomy.
2022 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-21-1494/coif). PT reports that he is supported by the scientific grant program of the Charles University Prague, Czech Republic (UNCE MED 02 and PROGRES Q38) and in the past received a part-time salary for lectures and presentations for the firms, Medtronic, B Braun and Abiomed. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Minimally Invasive and Full Sternotomy Aortic Valve Replacements Lead to Comparable Long-Term Outcomes in Elderly Higher-Risk Patients: A Propensity-Matched Comparison.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024 Mar 31;11(4):112. doi: 10.3390/jcdd11040112. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024. PMID: 38667730 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Aortic Valve Replacement through Full Sternotomy and Minimal Invasion (Ministernotomy).Medicina (Kaunas). 2018 Apr 28;54(2):26. doi: 10.3390/medicina54020026. Medicina (Kaunas). 2018. PMID: 30344257 Free PMC article.
-
Upper 'J' ministernotomy versus full sternotomy: an easier approach for aortic valve reoperation.J Heart Valve Dis. 2013 May;22(3):295-300. J Heart Valve Dis. 2013. PMID: 24151754
-
Minimal access versus conventional aortic valve replacement: a meta-analysis of propensity-matched studies.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2017 Oct 1;25(4):624-632. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivx212. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2017. PMID: 28962507 Review.
-
Minimally Invasive Aortic Valve Replacement: Cost-Benefit Analysis of Ministernotomy Versus Minithoracotomy Approach.J Heart Valve Dis. 2015 Sep;24(5):531-9. J Heart Valve Dis. 2015. PMID: 26897831 Review.
Cited by
-
Short-Term Outcomes of Partial Upper Ministernotomy for Aortic Valve Replacement Within the Learning Curve Context.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025 Jul 1;12(7):254. doi: 10.3390/jcdd12070254. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025. PMID: 40710779 Free PMC article.
-
Two-Stage Sternotomy Approach to Hostile Chest Reentry for Orthotopic Heart Transplantation.J Clin Med. 2025 Feb 14;14(4):1251. doi: 10.3390/jcm14041251. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40004782 Free PMC article.
-
Minimally Invasive and Full Sternotomy Aortic Valve Replacements Lead to Comparable Long-Term Outcomes in Elderly Higher-Risk Patients: A Propensity-Matched Comparison.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024 Mar 31;11(4):112. doi: 10.3390/jcdd11040112. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024. PMID: 38667730 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
