Ischemic Stroke-A Scientometric Analysis
- PMID: 35572940
- PMCID: PMC9096122
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.893121
Ischemic Stroke-A Scientometric Analysis
Abstract
Background: Stroke is the second leading cause of death world-wide. A comprehensive scientometric study regarding ischemic stroke research has not been performed yet. This study aims at investigating the global research output on ischemic stroke research.
Methods: All 21,115 articles regarding ischemic stroke were retrieved from the Web-of-Science-Core-Collection and analyzed regarding regional differences, the authors' sex, subtopics of stroke, as well as international research collaborations.
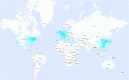
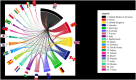
Results: A total of 132 different countries participated, with the USA contributing most publications with 4,614 (21.9%), followed by China with 3,872 (18.3%), and Germany with 1,120 (5.3%). Analyzing the scientific quality of different countries by H-index, the USA ranked first with an H-index of 202, followed by Germany (H-index 135) and the United Kingdom (UK;H-index 129). The most frequently used topic was "Clinical Neurology" with 9,028 publications. Among all first authors attributed to their sex, 32.3% of all first authors were female and 67.7% were male (4,335 vs. 9,097). The proportion of female last authors was comparatively lower at 22.4% (3,083 publications) compared with 77.6% male authors (10,658 publications). There was a broad network of international collaborations.
Conclusions: Research in ischemic stroke has substantially increased over time. Scientists from the USA have the highest number of publications, followed by China and Germany. Measured by the H-index, the USA held the highest publication quality, followed by Germany and the UK. The scientific landscape was male-dominated with 67.7% of all first authors being male. Worldwide international collaborations play a major role in ischemic stroke research.
Keywords: citation analysis; hemorrhagic; ischemic; research; stroke.
Copyright © 2022 Millenaar, Ragoschke-Schumm, Fehlmann, Raible, Lochner, Böhm, Fassbender, Keller, Mahfoud and Ukena.
Conflict of interest statement
DM has received honoraria from Bayer, Boston Scientific, and Daiichi Sankyo. MB receives honoraria for lectures and scientific advice from Abbott, Astra-Zeneca, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Medtronic, Novartis, Servier, and Vifor. FM has received scientific support and speaker honoraria from Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Medtronic, and ReCor Medical. CU received scientific support and speaker honorarium from Bayer, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Medtronic Inc., Recor Medical, and Pfizer. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kleindorfer DO, Towfighi A, Chaturvedi S, Cockroft KM, Gutierrez J, Lombardi-Hill D, et al. . 2021 Guideline for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack: a guideline from the American heart association/American stroke association. Stroke. (2021) 52:e364–467. 10.1161/STR.0000000000000375 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

