Whole genome sequencing of cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. CCCryo 231-06 using microfluidic single cell technology
- PMID: 35573199
- PMCID: PMC9095746
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104291
Whole genome sequencing of cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. CCCryo 231-06 using microfluidic single cell technology
Abstract
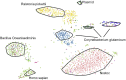
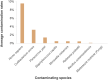
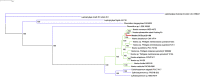
The Nostoc sp. strain CCCryo 231-06 is a cyanobacterial strain capable of surviving under extreme conditions and thus is of great interest for the astrobiology community. The knowledge of its complete genome sequence would serve as a guide for further studies. However, a major concern has been placed on the effects of contamination on the quality of sequencing data without a reference genome. Here, we report the use of microfluidic technology combined with single cell sequencing and de novo assembly to minimize the contamination and recover the complete genome of the Nostoc strain CCCryo 231-06 with high quality. 100% of the whole genome was recovered with all contaminants removed and a strongly supported phylogenetic tree. The data reported can be useful for comparative genomics for phylogenetic and taxonomic studies. The method used in this work can be applied to studies that require high-quality assemblies of genomes of unknown microorganisms.
Keywords: Astrobiology; Microbial genomics; Microbiology; Space sciences.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Andersson T., Ertürk Bergdahl G., Saleh K., Magnúsdóttir H., Stødkilde K., Andersen C.B.F., Lundqvist K., Jensen A., Brüggemann H., Lood R. Common skin bacteria protect their host from oxidative stress through secreted antioxidant RoxP. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:3596. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40471-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

