A Case Study on Integrating a New Key Event Into an Existing Adverse Outcome Pathway on Oxidative DNA Damage: Challenges and Approaches in a Data-Rich Area
- PMID: 35573276
- PMCID: PMC9097222
- DOI: 10.3389/ftox.2022.827328
A Case Study on Integrating a New Key Event Into an Existing Adverse Outcome Pathway on Oxidative DNA Damage: Challenges and Approaches in a Data-Rich Area
Abstract
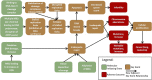
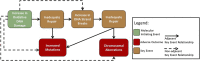
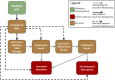
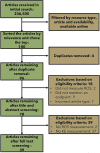
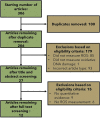
Adverse outcome pathways (AOPs) synthesize toxicological information to convey and weigh evidence in an accessible format. AOPs are constructed in modules that include key events (KEs) and key event relationships (KERs). This modular structure facilitates AOP expansion and network development. AOP development requires finding relevant information to evaluate the weight of evidence supporting each KER. To do this, the use of transparent/reproducible search methods, such as systematic review (SR), have been proposed. Applying SR to AOP development in a data-rich area is difficult as SR requires screening each article returned from a search. Here we describe a case study to integrate a single new KE into an existing AOP. We explored the use of SR concepts and software to conduct a transparent and documented literature search to identify empirical data supporting the incorporation of a new KE, increase in cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS), upstream of an existing AOP: "Oxidative DNA Damage Leading to Chromosomal Aberrations and Mutations". Connecting this KE to the AOP is supported by the development of five new KERs, the most important being the first adjacent KER (increase in ROS leading to oxidative DNA damage). We initially searched for evidence of all five KERs and screened 100 papers to develop a preliminary evidence map. After removing papers not containing relevant data based on our Population, Exposure, Comparator and Outcome statement, 39 articles supported one or more KERs; these primarily addressed temporal or dose concordance of the non-adjacent KERs with limited evidence supporting the first adjacent KER. We thus conducted a second focused set of searches using search terms for specific methodologies to measure these first two KEs. After screening, 12 articles were identified that contained quantitative evidence supporting the first adjacent KER. Given that integrating a new KE into an existing AOP requires the development of multiple KERs, this approach of building a preliminary evidence map, focusing evidence gathering on the first adjacent KER, and applying reproducible search strategies using specific methodologies for the first adjacent KER, enabled us to prioritize studies to support expansion of this data-rich AOP.
Keywords: DNA damage; adverse outcome pathways; genotoxicity; reactive oxygen species; toxicology.
Copyright © 2022 Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Challenges in the quantification approach to a radiation relevant adverse outcome pathway for lung cancer.Int J Radiat Biol. 2021;97(1):85-101. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2020.1820096. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Int J Radiat Biol. 2021. PMID: 32909875 Free PMC article.
-
A quantitative weight-of-evidence method for confidence assessment of adverse outcome pathway networks: A case study on chemical-induced liver steatosis.Toxicology. 2024 Jun;505:153814. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2024.153814. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Toxicology. 2024. PMID: 38677583
-
A case example of a radiation-relevant adverse outcome pathway to lung cancer.Int J Radiat Biol. 2021;97(1):68-84. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2019.1704913. Epub 2020 Jan 9. Int J Radiat Biol. 2021. PMID: 31846388
-
Development of an adverse outcome pathway for chemically induced hepatocellular carcinoma: case study of AFB1, a human carcinogen with a mutagenic mode of action.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2018 Apr;48(4):312-337. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2017.1423462. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29431554 Review.
-
Linking nanomaterial-induced mitochondrial dysfunction to existing adverse outcome pathways for chemicals.ALTEX. 2024 Jan 9;41(1):76-90. doi: 10.14573/altex.2305011. Epub 2023 Aug 21. ALTEX. 2024. PMID: 37606097 Review.
Cited by
-
AOP key event relationship report: Linking androgen receptor antagonism with nipple retention.Curr Res Toxicol. 2022 Aug 30;3:100085. doi: 10.1016/j.crtox.2022.100085. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36090961 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

