The Golgi Apparatus and its Next-Door Neighbors
- PMID: 35573670
- PMCID: PMC9096111
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.884360
The Golgi Apparatus and its Next-Door Neighbors
Abstract
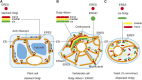
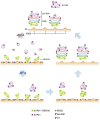
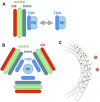
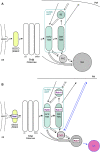
The Golgi apparatus represents a central compartment of membrane traffic. Its apparent architecture, however, differs considerably among species, from unstacked and scattered cisternae in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae to beautiful ministacks in plants and further to gigantic ribbon structures typically seen in mammals. Considering the well-conserved functions of the Golgi, its fundamental structure must have been optimized despite seemingly different architectures. In addition to the core layers of cisternae, the Golgi is usually accompanied by next-door compartments on its cis and trans sides. The trans-Golgi network (TGN) can be now considered as a compartment independent from the Golgi stack. On the cis side, the intermediate compartment between the ER and the Golgi (ERGIC) has been known in mammalian cells, and its functional equivalent is now suggested for yeast and plant cells. High-resolution live imaging is extremely powerful for elucidating the dynamics of these compartments and has revealed amazing similarities in their behaviors, indicating common mechanisms conserved along the long course of evolution. From these new findings, I would like to propose reconsideration of compartments and suggest a new concept to describe their roles comprehensively around the Golgi and in the post-Golgi trafficking.
Keywords: ERGIC; GECCO; Golgi; SCLIM; live imaging; membrane traffic; recycling endosome; trans-Golgi network.
Copyright © 2022 Nakano.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Spatiotemporal dissection of the Golgi apparatus and the ER-Golgi intermediate compartment in budding yeast.Elife. 2024 Mar 19;13:e92900. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92900. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38501165 Free PMC article.
-
The yeast endocytic early/sorting compartment exists as an independent sub-compartment within the trans-Golgi network.Elife. 2023 Jul 21;12:e84850. doi: 10.7554/eLife.84850. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37477116 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation of Trafficking Pathways at Golgi Entry Core Compartments and Post-Golgi Subdomains.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Dec 8;11:609516. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.609516. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 33363561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural evidence for multiple transport mechanisms through the Golgi in the pancreatic beta-cell line, HIT-T15.Biochem Soc Trans. 2001 Aug;29(Pt 4):461-7. doi: 10.1042/bst0290461. Biochem Soc Trans. 2001. PMID: 11498009
-
Plant TGNs: dynamics and physiological functions.Histochem Cell Biol. 2013 Sep;140(3):341-5. doi: 10.1007/s00418-013-1116-7. Epub 2013 Jul 6. Histochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23832380 Review.
Cited by
-
Interactome of Arabidopsis ATG5 Suggests Functions beyond Autophagy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 1;24(15):12300. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512300. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569688 Free PMC article.
-
The link between the trans-Golgi network and tumour progression.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Apr 28;52(1):435. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10548-6. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40293576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatiotemporal dissection of the Golgi apparatus and the ER-Golgi intermediate compartment in budding yeast.Elife. 2024 Mar 19;13:e92900. doi: 10.7554/eLife.92900. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38501165 Free PMC article.
-
Endosidin 5 disruption of the Golgi apparatus and extracellular matrix secretion in the unicellular charophyte Penium margaritaceum.Ann Bot. 2023 Jul 10;131(6):967-983. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcad054. Ann Bot. 2023. PMID: 37076269 Free PMC article.
-
ER-to-Golgi trafficking through a dynamic intermediate cis-Golgi tubular network in Arabidopsis.Nat Cell Biol. 2025 Mar;27(3):424-437. doi: 10.1038/s41556-025-01624-x. Epub 2025 Feb 25. Nat Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 40000850
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

