Dissection of the microRNA Network Regulating Hedgehog Signaling in Drosophila
- PMID: 35573695
- PMCID: PMC9096565
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.866491
Dissection of the microRNA Network Regulating Hedgehog Signaling in Drosophila
Abstract
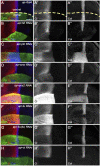
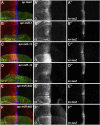
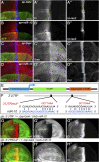
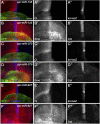
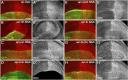
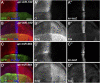
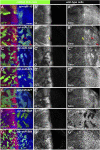
The evolutionarily conserved Hedgehog (Hh) signaling plays a critical role in embryogenesis and adult tissue homeostasis. Aberrant Hh signaling often leads to various forms of developmental anomalies and cancer. Since altered microRNA (miRNA) expression is associated with developmental defects and tumorigenesis, it is not surprising that several miRNAs have been found to regulate Hh signaling. However, these miRNAs are mainly identified through small-scale in vivo screening or in vitro assays. As miRNAs preferentially reduce target gene expression via the 3' untranslated region, we analyzed the effect of reduced expression of core components of the Hh signaling cascade on downstream signaling activity, and generated a transgenic Drosophila toolbox of in vivo miRNA sensors for core components of Hh signaling, including hh, patched (ptc), smoothened (smo), costal 2 (cos2), fused (fu), Suppressor of fused (Su(fu)), and cubitus interruptus (ci). With these tools in hand, we performed a genome-wide in vivo miRNA overexpression screen in the developing Drosophila wing imaginal disc. Of the twelve miRNAs identified, seven were not previously reported in the in vivo Hh regulatory network. Moreover, these miRNAs may act as general regulators of Hh signaling, as their overexpression disrupts Hh signaling-mediated cyst stem cell maintenance during spermatogenesis. To identify direct targets of these newly discovered miRNAs, we used the miRNA sensor toolbox to show that miR-10 and miR-958 directly target fu and smo, respectively, while the other five miRNAs act through yet-to-be-identified targets other than the seven core components of Hh signaling described above. Importantly, through loss-of-function analysis, we found that endogenous miR-10 and miR-958 target fu and smo, respectively, whereas deletion of the other five miRNAs leads to altered expression of Hh signaling components, suggesting that these seven newly discovered miRNAs regulate Hh signaling in vivo. Given the powerful effects of these miRNAs on Hh signaling, we believe that identifying their bona fide targets of the other five miRNAs will help reveal important new players in the Hh regulatory network.
Keywords: Drosophila wing; hedgehog signaling; in vivo miRNA sensor toolbox; miR-10; miR-958.
Copyright © 2022 He, Fan, Wang, Liu and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Drosophila miR-960 negatively regulates Hedgehog signaling by suppressing Smoothened, Costal-2 and Fused.Cell Signal. 2013 May;25(5):1301-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.01.023. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23385085
-
Evidence for a novel feedback loop in the Hedgehog pathway involving Smoothened and Fused.Curr Biol. 2007 Aug 7;17(15):1326-33. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.06.059. Epub 2007 Jul 19. Curr Biol. 2007. PMID: 17658259
-
Differential regulation of Hedgehog target gene transcription by Costal2 and Suppressor of Fused.Development. 2005 Mar;132(6):1401-12. doi: 10.1242/dev.01689. Development. 2005. PMID: 15750186
-
Regulation of Hedgehog signaling: a complex story.Biochem Pharmacol. 2004 Mar 1;67(5):805-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2004.01.002. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15104233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Hedgehog Signal Transduction by Ubiquitination and Deubiquitination.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 11;22(24):13338. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413338. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948134 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of salivary miRNAs in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal disorders: a mini-review of available evidence.Front Genet. 2023 Jun 29;14:1228482. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1228482. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37456668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biogenesis of circular RNAs in vitro and in vivo from the Drosophila Nk2.1/scarecrow gene.G3 (Bethesda). 2025 May 8;15(5):jkaf055. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkaf055. G3 (Bethesda). 2025. PMID: 40071305 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo AGO-APP identifies a module of microRNAs cooperatively preserving neural progenitors.PLoS Genet. 2025 Apr 29;21(4):e1011680. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011680. eCollection 2025 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2025. PMID: 40299997 Free PMC article.
-
A new experimental evidence-weighted signaling pathway resource in FlyBase.Development. 2024 Feb 1;151(3):dev202255. doi: 10.1242/dev.202255. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Development. 2024. PMID: 38230566 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

