Integrating Ethics and Career Futures with Technical Learning to Promote AI Literacy for Middle School Students: An Exploratory Study
- PMID: 35573722
- PMCID: PMC9084886
- DOI: 10.1007/s40593-022-00293-3
Integrating Ethics and Career Futures with Technical Learning to Promote AI Literacy for Middle School Students: An Exploratory Study
Abstract
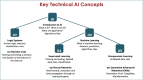
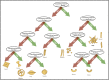
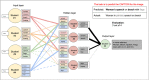
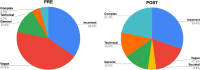
The rapid expansion of artificial intelligence (AI) necessitates promoting AI education at the K-12 level. However, educating young learners to become AI literate citizens poses several challenges. The components of AI literacy are ill-defined and it is unclear to what extent middle school students can engage in learning about AI as a sociotechnical system with socio-political implications. In this paper we posit that students must learn three core domains of AI: technical concepts and processes, ethical and societal implications, and career futures in the AI era. This paper describes the design and implementation of the Developing AI Literacy (DAILy) workshop that aimed to integrate middle school students' learning of the three domains. We found that after the workshop, most students developed a general understanding of AI concepts and processes (e.g., supervised learning and logic systems). More importantly, they were able to identify bias, describe ways to mitigate bias in machine learning, and start to consider how AI may impact their future lives and careers. At exit, nearly half of the students explained AI as not just a technical subject, but one that has personal, career, and societal implications. Overall, this finding suggests that the approach of incorporating ethics and career futures into AI education is age appropriate and effective for developing AI literacy among middle school students. This study contributes to the field of AI Education by presenting a model of integrating ethics into the teaching of AI that is appropriate for middle school students.
Keywords: AI ethics; Bias; Career implications; Middle school education; Sociotechnical systems.
© International Artificial Intelligence in Education Society 2022.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Artificial intelligence in education: Addressing ethical challenges in K-12 settings.AI Ethics. 2022;2(3):431-440. doi: 10.1007/s43681-021-00096-7. Epub 2021 Sep 22. AI Ethics. 2022. PMID: 34790956 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AI + Ethics Curricula for Middle School Youth: Lessons Learned from Three Project-Based Curricula.Int J Artif Intell Educ. 2022 Aug 1:1-59. doi: 10.1007/s40593-022-00298-y. Online ahead of print. Int J Artif Intell Educ. 2022. PMID: 35935456 Free PMC article.
-
Contextualizing AI Education for K-12 Students to Enhance Their Learning of AI Literacy Through Culturally Responsive Approaches.Kunstliche Intell (Oldenbourg). 2021;35(2):153-161. doi: 10.1007/s13218-021-00737-3. Epub 2021 Aug 6. Kunstliche Intell (Oldenbourg). 2021. PMID: 34376922 Free PMC article.
-
[Embracing the Era of Artificial Intelligence: Innovation and Preparation in Nursing Education].Hu Li Za Zhi. 2024 Apr;71(2):4-5. doi: 10.6224/JN.202404_71(2).01. Hu Li Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38532668 Chinese.
-
Teaching, Learning and Assessing Anatomy with Artificial Intelligence: The Road to a Better Future.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 31;19(21):14209. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192114209. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36361089 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of artificial intelligence on human loss in decision making, laziness and safety in education.Humanit Soc Sci Commun. 2023;10(1):311. doi: 10.1057/s41599-023-01787-8. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Humanit Soc Sci Commun. 2023. PMID: 37325188 Free PMC article.
-
Path of career planning and employment strategy based on deep learning in the information age.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 15;19(10):e0308654. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308654. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39405324 Free PMC article.
-
Perceived support and AI literacy: the mediating role of psychological needs satisfaction.Front Psychol. 2024 Jun 14;15:1415248. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1415248. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38947906 Free PMC article.
-
Current and future applications of artificial intelligence in surgery: implications for clinical practice and research.Front Surg. 2024 May 9;11:1393898. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1393898. eCollection 2024. Front Surg. 2024. PMID: 38783862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethical issues of the use of AI-driven mobile apps for education.Front Public Health. 2023 Jan 11;10:1118116. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1118116. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36711343 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali, S., Payne, B. H., Williams, R., Park, H. W., & Breazeal, C. (2019). Constructionism, ethics, and creativity: Developing primary and middle school artificial intelligence education. In International workshop on education in artificial intelligence K-12 (EDUAI'19) (pp. 1–4).
-
- Ali, S., DiPaola, D., Lee, I., Hong, J., & Breazeal, C. (2021). Exploring Generative Models with Middle School Students. In Proceedings of the 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp. 1–13).
-
- Almstrum, V. L., Henderson, P. B., Harvey, V., Heeren, C., Marion, W., Riedesel, C., Soh, L.-K., & Tew, A. E. (2006). Concept inventories in computer science for the topic discrete mathematics. In Working group reports on ITiCSE on Innovation and technology in computer science education (pp. 132–145).
-
- Badham, R., Clegg, C., & Wall, T. (2000). Socio-technical theory. Handbook of Ergonomics. John Wiley.
-
- Boss JA. The effect of community service work on the moral development of college ethics students. Journal of Moral Education. 1994;23(2):183–198. doi: 10.1080/0305724940230206. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
