Quantification of vascular networks in photoacoustic mesoscopy
- PMID: 35574188
- PMCID: PMC9095888
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pacs.2022.100357
Quantification of vascular networks in photoacoustic mesoscopy
Abstract
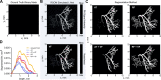
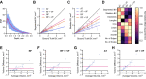
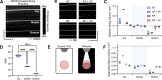
Mesoscopic photoacoustic imaging (PAI) enables non-invasive visualisation of tumour vasculature. The visual or semi-quantitative 2D measurements typically applied to mesoscopic PAI data fail to capture the 3D vessel network complexity and lack robust ground truths for assessment of accuracy. Here, we developed a pipeline for quantifying 3D vascular networks captured using mesoscopic PAI and tested the preservation of blood volume and network structure with topological data analysis. Ground truth data of in silico synthetic vasculatures and a string phantom indicated that learning-based segmentation best preserves vessel diameter and blood volume at depth, while rule-based segmentation with vesselness image filtering accurately preserved network structure in superficial vessels. Segmentation of vessels in breast cancer patient-derived xenografts (PDXs) compared favourably to ex vivo immunohistochemistry. Furthermore, our findings underscore the importance of validating segmentation methods when applying mesoscopic PAI as a tool to evaluate vascular networks in vivo.
Keywords: Photoacoustic imaging; Segmentation; Topology; Vasculature.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Sarah Bohndiek reports a relationship with EPFL Center for Biomedical Imaging that includes: speaking and lecture fees. Sarah Bohndiek reports a relationship with PreXion Inc that includes: funding grants. Sarah Bohndiek reports a relationship with iThera Medical GmbH that includes: non-financial support. The other authors have no conflict of interest related to the present manuscript to disclose.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

