Dissecting the phenotypic variability of osteogenesis imperfecta
- PMID: 35575034
- PMCID: PMC9150118
- DOI: 10.1242/dmm.049398
Dissecting the phenotypic variability of osteogenesis imperfecta
Abstract
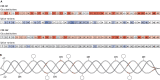
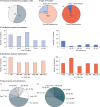
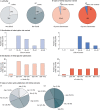
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a heterogeneous family of collagen type I-related diseases characterized by bone fragility. OI is most commonly caused by single-nucleotide substitutions that replace glycine residues or exon splicing defects in the COL1A1 and COL1A2 genes that encode the α1(I) and α2(I) collagen chains. Mutant collagen is partially retained intracellularly, impairing cell homeostasis. Upon secretion, it assembles in disorganized fibrils, altering mineralization. OI is characterized by a wide range of clinical outcomes, even in the presence of identical sequence variants. Given the heterotrimeric nature of collagen I, its amino acid composition and the peculiarity of its folding, several causes may underlie the phenotypic variability of OI. A deep analysis of entries regarding glycine and splice site collagen substitution of the largest publicly available patient database reveals a higher risk of lethal phenotype for carriers of variants in α1(I) than in α2(I) chain. However, splice site variants are predominantly associated with lethal phenotype when they occur in COL1A2. In addition, lethality is increased when mutations occur in regions of importance for extracellular matrix interactions. Both extracellular and intracellular determinants of OI clinical severity are discussed in light of the findings from in vitro and in vivo OI models. Combined with meticulous tracking of clinical cases via a publicly available database, the available OI animal models have proven to be a unique tool to shed light on new modulators of phenotype determination for this rare heterogeneous disease.
Keywords: Bone; Osteogenesis imperfecta; Phenotypic variability.
© 2022. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bank, R. A., Tekoppele, J. M., Janus, G. J. M., Wassen, M. H. M., Pruijs, H. E. H., Van der Sluijs, H. A. H. and Sakkers, R. J. B. (2000). Pyridinium cross-links in bone of patients with osteogenesis imperfecta: evidence of a normal intrafibrillar collagen packing. J. Bone Miner. Res. 15, 1330-1336. 10.1359/jbmr.2000.15.7.1330 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barnes, A. M., Ashok, A., Makareeva, E. N., Brusel, M., Cabral, W. A., Weis, M., Moali, C., Bettler, E., Eyre, D. R., Cassella, J. P.et al. (2019). COL1A1 C-propeptide mutations cause ER mislocalization of procollagen and impair C-terminal procollagen processing. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1865, 2210-2223. 10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.04.018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Besio, R., Iula, G., Garibaldi, N., Cipolla, L., Sabbioneda, S., Biggiogera, M., Marini, J. C., Rossi, A. and Forlino, A. (2018). 4-PBA ameliorates cellular homeostasis in fibroblasts from osteogenesis imperfecta patients by enhancing autophagy and stimulating protein secretion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1864, 1642-1652. 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.02.002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

