Parent socialization and anti-racist ideology development in White youth: Do peer and parenting contexts matter?
- PMID: 35575149
- PMCID: PMC10409607
- DOI: 10.1111/cdev.13788
Parent socialization and anti-racist ideology development in White youth: Do peer and parenting contexts matter?
Abstract
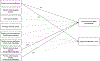
The development of anti-racist ideology in adolescence and emerging adulthood is informed by parent socialization, parenting style, and cross-race friendships. This study used longitudinal, multi-reporter survey data from White youth and their parents in Maryland to examine links between parents' racial attitudes when youth were in eleventh grade in 1996 (N = 453; 52% female; Mage = 17.12) and the youths' anti-racist ideology (acknowledgment of anti-Black discrimination and support for affirmative action) 1 year after high school in 1998. This study also examined whether these associations varied based on authoritative parenting and the number of cross-race friendships. Positive parent racial attitudes toward racially and ethnically minoritized populations predicted higher anti-racist ideology in the independent contexts of more cross-race friendships and low authoritative parenting.
© 2022 The Authors. Child Development © 2022 Society for Research in Child Development.
Figures



Similar articles
-
An Observational Approach to Examining White Parents' Racial Socialization Practices With Adolescent Youth.J Res Adolesc. 2022 Sep;32(3):883-895. doi: 10.1111/jora.12766. Epub 2022 May 26. J Res Adolesc. 2022. PMID: 35615942 Free PMC article.
-
Parenting in African American families: Profiles of general and culturally specific dimensions of parent-adolescent relationships during late adolescence.J Res Adolesc. 2024 Sep;34(3):928-943. doi: 10.1111/jora.12975. Epub 2024 Jun 26. J Res Adolesc. 2024. PMID: 38923203
-
Embracing Race, Resisting Oppression: African American Parents as Experienced Guides for Navigating Racial Oppression: Dismantling Systems of Racism and Oppression during Adolescence.J Res Adolesc. 2022 Mar;32(1):115-133. doi: 10.1111/jora.12712. Epub 2021 Dec 23. J Res Adolesc. 2022. PMID: 34939723
-
Racial discrimination and alcohol problems among African American young adults: Examining the moderating effects of racial socialization by parents and friends.Cultur Divers Ethnic Minor Psychol. 2020 Apr;26(2):260-270. doi: 10.1037/cdp0000294. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Cultur Divers Ethnic Minor Psychol. 2020. PMID: 31328948 Free PMC article.
-
Intervention induced changes on parenting practices, youth self-pride and sexual norms to reduce HIV-related behaviors among rural African American youths.J Youth Adolesc. 2011 Sep;40(9):1147-63. doi: 10.1007/s10964-011-9642-x. Epub 2011 Mar 5. J Youth Adolesc. 2011. PMID: 21373904 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aboud F, Mendelson M, & Purdy K. (2003). Cross-race peer relations and friendship quality. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 27(2), 165–173. 10.1090/01650250244000164 - DOI
-
- Aiken LS, West SG, & Reno RR (1991). Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. Sage.
-
- Allport GW (1954). The nature of prejudice. Addison Wesley.
-
- Arbuckle JL (1996). Full information estimation in the presence of incomplete data. In Marcoulides GA & Schumacker RE (Eds.), Advanced structural equation modeling: Issues and techniques (pp. 243–277). Psychology Press.
-
- Atwell AC (2014). When “being down” isn’t enough: Examining White anti-racism and racial integration in the era of colorblindness [Masters thesis, Georgia State University]. https://scholarworks.gsu.edu/sociology_theses/48
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

