Noise exposure and its relationship with postinfarction cardiac remodeling: implications for NLRP3 inflammasome activation
- PMID: 35575239
- PMCID: PMC9275894
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2073126
Noise exposure and its relationship with postinfarction cardiac remodeling: implications for NLRP3 inflammasome activation
Abstract
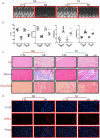
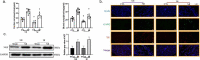
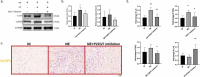
In recent years, high-decibel noise has emerged as a causative risk factor for ischemic heart disease. Massive noise overdose is associated with increased endocrine, neural, and immune stress responses. The NLRP3 (nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, leucine-rich repeat, and pyrin domain containing 3) inflammasome, the most characterized supramolecular complex and a potent mediator of inflammatory signaling, has been reported to be a marker of increased ischemic heart disease vulnerability. Our study evaluated the association of noise exposure with postinfarction cardiac remodeling and its effect on NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Rats were exposed to a noisy environment (14 days, 24 h/per day, 70 ± 5 dB), and speck formation by the NLRP3 inflammasome scaffold protein ASC (apoptosis-associated speck-like protein) was assessed by confocal immunofluorescence. Echocardiography, pathological analysis, and in vivo electrophysiology were performed. Our results revealed the improved postinfarction cardiac function, mitigated fibrosis, and decreased arrhythmia vulnerability and sympathetic sprouting in low-environment noise groups. Moreover, western blotting of NLRP3, caspase-1, ASC, IL-1β, and IL-18 and confocal microscopy of ASC speck showed that the priming and activation of NLRP3 inflammasome were higher in the NE group than in the NI group. In conclusion, our findings reveal a previously unidentified association between NLRP3 inflammasome activation and noise exposure, underscoring the significance of effective noise prevention in improving postinfarction prognosis.
Keywords: Myocardial infarction; NLRP3 inflammasome; inflammation; noise exposure; purinergic signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors disclosed no relevant relationships.
Figures




References
-
- Peterson EA, Augenstein JS, Tanis DC, et al. Noise raises blood pressure without impairing auditory sensitivity. Science. 1981;211(4489):1450–1452. - PubMed
-
- Alves-Pereira M, Castelo Branco NAA.. Vibroacoustic disease: biological effects of infrasound and low-frequency noise explained by mechanotransduction cellular signaling. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2007;93:256–279. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
