Thoracic imaging tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19
- PMID: 35575286
- PMCID: PMC9109458
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub5
Thoracic imaging tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19
Abstract
Background: Our March 2021 edition of this review showed thoracic imaging computed tomography (CT) to be sensitive and moderately specific in diagnosing COVID-19 pneumonia. This new edition is an update of the review.
Objectives: Our objectives were to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of thoracic imaging in people with suspected COVID-19; assess the rate of positive imaging in people who had an initial reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) negative result and a positive RT-PCR result on follow-up; and evaluate the accuracy of thoracic imaging for screening COVID-19 in asymptomatic individuals. The secondary objective was to assess threshold effects of index test positivity on accuracy.
Search methods: We searched the COVID-19 Living Evidence Database from the University of Bern, the Cochrane COVID-19 Study Register, The Stephen B. Thacker CDC Library, and repositories of COVID-19 publications through to 17 February 2021. We did not apply any language restrictions.
Selection criteria: We included diagnostic accuracy studies of all designs, except for case-control, that recruited participants of any age group suspected to have COVID-19. Studies had to assess chest CT, chest X-ray, or ultrasound of the lungs for the diagnosis of COVID-19, use a reference standard that included RT-PCR, and report estimates of test accuracy or provide data from which we could compute estimates. We excluded studies that used imaging as part of the reference standard and studies that excluded participants with normal index test results.
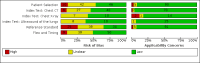
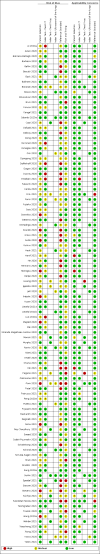
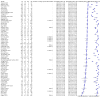
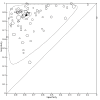
Data collection and analysis: The review authors independently and in duplicate screened articles, extracted data and assessed risk of bias and applicability concerns using QUADAS-2. We presented sensitivity and specificity per study on paired forest plots, and summarized pooled estimates in tables. We used a bivariate meta-analysis model where appropriate.
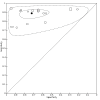
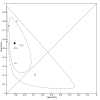
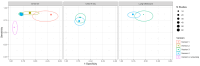
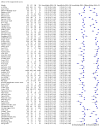
Main results: We included 98 studies in this review. Of these, 94 were included for evaluating the diagnostic accuracy of thoracic imaging in the evaluation of people with suspected COVID-19. Eight studies were included for assessing the rate of positive imaging in individuals with initial RT-PCR negative results and positive RT-PCR results on follow-up, and 10 studies were included for evaluating the accuracy of thoracic imaging for imagining asymptomatic individuals. For all 98 included studies, risk of bias was high or unclear in 52 (53%) studies with respect to participant selection, in 64 (65%) studies with respect to reference standard, in 46 (47%) studies with respect to index test, and in 48 (49%) studies with respect to flow and timing. Concerns about the applicability of the evidence to: participants were high or unclear in eight (8%) studies; index test were high or unclear in seven (7%) studies; and reference standard were high or unclear in seven (7%) studies. Imaging in people with suspected COVID-19 We included 94 studies. Eighty-seven studies evaluated one imaging modality, and seven studies evaluated two imaging modalities. All studies used RT-PCR alone or in combination with other criteria (for example, clinical signs and symptoms, positive contacts) as the reference standard for the diagnosis of COVID-19. For chest CT (69 studies, 28285 participants, 14,342 (51%) cases), sensitivities ranged from 45% to 100%, and specificities from 10% to 99%. The pooled sensitivity of chest CT was 86.9% (95% confidence interval (CI) 83.6 to 89.6), and pooled specificity was 78.3% (95% CI 73.7 to 82.3). Definition for index test positivity was a source of heterogeneity for sensitivity, but not specificity. Reference standard was not a source of heterogeneity. For chest X-ray (17 studies, 8529 participants, 5303 (62%) cases), the sensitivity ranged from 44% to 94% and specificity from 24 to 93%. The pooled sensitivity of chest X-ray was 73.1% (95% CI 64. to -80.5), and pooled specificity was 73.3% (95% CI 61.9 to 82.2). Definition for index test positivity was not found to be a source of heterogeneity. Definition for index test positivity and reference standard were not found to be sources of heterogeneity. For ultrasound of the lungs (15 studies, 2410 participants, 1158 (48%) cases), the sensitivity ranged from 73% to 94% and the specificity ranged from 21% to 98%. The pooled sensitivity of ultrasound was 88.9% (95% CI 84.9 to 92.0), and the pooled specificity was 72.2% (95% CI 58.8 to 82.5). Definition for index test positivity and reference standard were not found to be sources of heterogeneity. Indirect comparisons of modalities evaluated across all 94 studies indicated that chest CT and ultrasound gave higher sensitivity estimates than X-ray (P = 0.0003 and P = 0.001, respectively). Chest CT and ultrasound gave similar sensitivities (P=0.42). All modalities had similar specificities (CT versus X-ray P = 0.36; CT versus ultrasound P = 0.32; X-ray versus ultrasound P = 0.89). Imaging in PCR-negative people who subsequently became positive For rate of positive imaging in individuals with initial RT-PCR negative results, we included 8 studies (7 CT, 1 ultrasound) with a total of 198 participants suspected of having COVID-19, all of whom had a final diagnosis of COVID-19. Most studies (7/8) evaluated CT. Of 177 participants with initially negative RT-PCR who had positive RT-PCR results on follow-up testing, 75.8% (95% CI 45.3 to 92.2) had positive CT findings. Imaging in asymptomatic PCR-positive people For imaging asymptomatic individuals, we included 10 studies (7 CT, 1 X-ray, 2 ultrasound) with a total of 3548 asymptomatic participants, of whom 364 (10%) had a final diagnosis of COVID-19. For chest CT (7 studies, 3134 participants, 315 (10%) cases), the pooled sensitivity was 55.7% (95% CI 35.4 to 74.3) and the pooled specificity was 91.1% (95% CI 82.6 to 95.7).
Authors' conclusions: Chest CT and ultrasound of the lungs are sensitive and moderately specific in diagnosing COVID-19. Chest X-ray is moderately sensitive and moderately specific in diagnosing COVID-19. Thus, chest CT and ultrasound may have more utility for ruling out COVID-19 than for differentiating SARS-CoV-2 infection from other causes of respiratory illness. The uncertainty resulting from high or unclear risk of bias and the heterogeneity of included studies limit our ability to confidently draw conclusions based on our results.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. on behalf of The Cochrane Collaboration.
Conflict of interest statement
Sanam Ebrahimzadeh has no known conflicts of interest.
Nayaar Islam has no known conflicts of interest.
Haben Dawit has no known conflicts of interest.
Jean‐Paul Salameh has no known conflicts of interest.
Sakib Kazi has no known conflicts of interest.
Nicholas Fabiano has no known conflicts of interest.
Lee Treanor has no known conflicts of interest.
Marissa Absi has no known conflicts of interest.
Faraz Ahmad has no known conflicts of interest.
Paul Rooprai has no known conflicts of interest.
Ahmed Al Khalil has no known conflicts of interest.
Kelly Harper has no known conflicts of interest.
Neil Kamra has no known conflicts of interest.
Mariska MG Leeflang has no known conflicts of interest.
Lotty Hooft has no known conflicts of interest.
Christian B van der Pol has no known conflicts of interest.
Ross Prager has no known conflicts of interest.
Samanjit S Hare has no known conflicts of interest.
Carole Dennie has no known conflicts of interest.
René Spijker: the Dutch Cochrane Centre (DCC) has received grants for performing commissioned systematic reviews. In no situation did the commissioner have any influence on the results of the work.
Jonathan J Deeks has no known conflicts of interest.
Jacqueline Dinnes has no known conflicts of interest.
Kevin Jenniskens has no known conflicts of interest.
Daniel Korevaar has no known conflicts of interest.
Jérémie F Cohen has no known conflicts of interest.
Ann Van den Bruel has no known conflicts of interest.
Yemisi Takwoingi has no known conflicts of interest.
Janneke van de Wijgert has no known conflicts of interest.
Junfeng Wang received a consultancy fee from Biomind, an Artificial Intelligence (AI) company providing machine intelligence solutions in medical imaging. The consultancy service was about design of clinical studies, not related to this review. The company had no influence on the results of the work.
Elena Pena has no known conflicts of interest.
Sandra Sabongui has no known conflicts of interest.
Matthew McInnes has no known conflicts of interest.
Figures








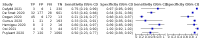







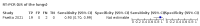

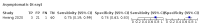

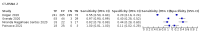


Update of
-
Thoracic imaging tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 16;3(3):CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 16;5:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub5. PMID: 33724443 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Ai 2020a {published data only}
Aslan 2020 {published data only}
Bahrami‐Motlagh 2020 {published data only}
Barbosa 2020 {published data only}
Bellini 2020 {published data only}
-
- Bellini D, Panvini N, Rengo M, Vicini S, Lichtner M, Tieghi T, et al.Diagnostic accuracy and interobserver variability of CO-RADS in patients with suspected coronavirus disease-2019: a multireader validation study. European Radiology 2020 Sep 23;31(4):1932-40. [DOI: 10.1007/s00330-020-07273-y] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Besutti 2020 {published data only}
Bock 2021 {published data only}
-
- Bock A, Lassen AT, Laursen CB, Posth S.Lung ultrasound as a prognostic tool in emergency patients clinically suspected of COVID-19. Danish Medical Journal 2021 Jan 7;68(2):A07200551. - PubMed
Bollineni 2021 {published data only}
Borakati 2020 {published data only}
Bosso 2021 {published data only}
Boussouar 2020 {published data only}
-
- Boussouar S, Wagner M, Donciu V, Pasi N, Salem JE, Renard-Penna R, et al.Diagnostic performance of chest computed tomography during the epidemic wave of COVID-19 varied as a function of time since the beginning of the confinement in France. PLOS One 2020 Nov 23;15(11):e0242840. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242840] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Brun 2021 {published data only}
Caruso 2020 {published data only}
Cengel 2021 {published data only}
-
- Cengel F, Gurkan O, Calik M, Demirkol MA, Sargin Altunok E, Kaya MF, et al.Diagnosis of the coronavirus disease 2019 with chest computed tomography: a retrospective inter-observer agreement study between radiologists and clinicians. Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine 2021 Jan 1;28(1):15-21. [DOI: 10.1177/1024907920968648] - DOI
Colombi 2020a {published data only}
-
- Colombi D, Petrini M, Maffi G, Villani GD, Bodini FC, Morelli N, et al.Comparison of admission chest computed tomography and lung ultrasound performance for diagnosis of COVID-19 pneumonia in populations with different disease prevalence. European Journal of Radiology 2020 Dec 1;133:109344. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109344] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Cozzi 2020 {published data only}
Dafydd 2021 {published data only}
-
- Ap Dafydd D, O'Mahony M, Jhanji S, Devaraj A, Allum W, Nicol D, et al.The role of CT chest in screening for asymptomatic COVID-19 infection in self-isolating patients prior to elective oncological surgery: findings from a UK Cancer Hub. British Institute of Radiology 2021 Jan 1;94(1117):20200994. [DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20200994] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Debray 2020 {published data only}
Deng 2020 {published data only}
-
- Deng Z, Zhang X, Li Y, Xu H, Gang Y, Wang H, et al.[The value of chest CT screening in the early stage of a new coronaviruspneumonia outbreak]. Chinese Journal of Radiology 2020 Mar 01;5(54):430-4. [DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112149-20200218-00187] - DOI
De Smet 2020 {published data only}
-
- Smet KD, Smet DD, Demedts I, Bouckaert B, Ryckaert T, Laridon E, et al.Diagnostic power of chest CT for COVID-19: to screen or not to screen. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: 10.1101/2020.05.18.20097444] - DOI
Dimeglio 2021 {published data only}
Dini 2020 {published data only}
Djangang 2020 {published data only}
Dofferhoff 2020 {published data only}
-
- Dofferhoff AS, Swinkels A, Sprong T, Berk Y, Spanbroek M, Nabuurs-Franssen MH, et al.Diagnostic algorithm for COVID-19 at the ER. Nederlands Tijdschrift voor Geneeskunde 2020;164:D5042. - PubMed
Dogan 2020 {published data only}
-
- Doğan D, Cüce F, Akay S, Ayaz T, Kinik D, Savaşçi Ü et al.Normal chest CT prevalence in coronavirus disease 2019 (covid-19) patients: A report of 791 cases. Acta Medica Mediterranea 2020 Sep 21;36(5):2917-21. [DOI: 10.19193/0393-6384_2020_5_447] - DOI
Ducray 2020 {published data only}
-
- Ducray V, Vlachomitrou AS, Bouscambert-Duchamp M, Si-Mohamed S, Gouttard S, Mansuy A, et al.Chest CT for rapid triage of patients in multiple emergency departments during COVID-19 epidemic: experience report from a large French university hospital. European Radiology 2020;31(2):795-803. [DOI: 10.1007/s00330-020-07154-4] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Erxleben 2021 {published data only}
Falaschi 2020 {published data only}
-
- Falaschi Z, Danna PS, Arioli R, Pasché A, Zagaria D, Percivale I, et al.Chest CT accuracy in diagnosing COVID-19 during the peak of the Italian epidemic: a retrospective correlation with RT-PCR testing and analysis of discordant cases. European Journal of Radiology 2020;130:109192. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109192] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Ferda 2020 {published data only}
-
- Ferda J, Vítovec M, Baxa J, Sedláček D, Havel D, Topolčan O, et al.Chest ct: A valuable tool in discrimination of covid-19 pneumonia, community acquired pneumonia and the other pathologies in slow epidemic phase. Ceska Radiologie 2020;74(3):171-9.
Fink 2021 {published data only}
-
- Fink N, Rueckel J, Kaestle S, Schwarze V, Gresser E, Hoppe B, et al.Evaluation of patients with respiratory infections during the first pandemic wave in Germany: characteristics of COVID-19 versus non-COVID-19 patients. BMC Infectious Diseases 2021 Feb 10;21(1):167. [DOI: 10.1186/s12879-021-05829-x] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Fonsi 2020 {published data only}
Fujioka 2020 {published data only}
Gaia 2020 {published data only}
-
- Gaia C, Maria Chiara C, Silvia L, Chiara A, Maria Luisa DC, Giulia B, et al.Chest CT for early detection and management of coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a report of 314 patients admitted to Emergency Department with suspected pneumonia. Radiologia Medica 2020;125(10):931-42. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Giannitto 2020 {published data only}
Gietema 2020 {published data only}
Gil‐Rodrigo 2020 {published data only}
-
- Gil-Rodrigo A, Llorens P, Martínez-Buendía C, Luque-Hernández M-J, Espinosa B, Ramos-Rincón JM.Diagnostic yield of point-of-care ultrasound imaging of the lung in patients with COVID-19. Emergencias 2020 Sep;32(5):340-4. - PubMed
Grando 2020 {published data only}
-
- Grando RD, Brentano VB, Zanardo AP, Hertz FT, Júnior LC, Prietto dos Santos JF, et al.Clinical usefulness of tomographic standards for COVID-19 pneumonia diagnosis: Experience from a Brazilian reference center. Brazilian Journal of Infectious Diseases 2020 Nov;24(6):524-33. [DOI: 10.1016/j.bjid.2020.10.002] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Gross 2021 {published data only}
-
- Gross A, Heine G, Schwarz M, Thiemig D, Gläser S, Albrecht T.Structured reporting of chest CT provides high sensitivity and specificity for early diagnosis of COVID-19 in a clinical routine setting. British Journal of Radiology 2021 Jan 1;94(1117):20200574. [DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20200574] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Guillo 2020 {published data only}
-
- Guillo E, Bedmar Gomez I, Dangeard S, Bennani S, Saab I, Tordjman M, et al.COVID-19 pneumonia: diagnostic and prognostic role of CT based on a retrospective analysis of 214 consecutive patients from Paris, France. European Journal of Radiology 2020;131:109209. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109209] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Gumus 2020 {published data only}
Haak 2021 {published data only}
Hanif 2021 {published data only}
He 2020 {published data only}
-
- He J-L, Luo L, Luo Z-D, Lyu J-X, Ng M-Y, Shen X-P, et al.Diagnostic performance between CT and initial real-time RT-PCR for clinically suspected 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) patients outside Wuhan, China. Respiratory Medicine 2020 Jul;168:105980. [DOI: 10.1016/j.rmed.2020.105980] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Hermans 2020 {published data only}
Hernigou 2020 {published data only}
-
- Hernigou J, Cornil F, Poignard A, El Bouchaibi S, Mani J, Naouri JF, et al.Thoracic computerised tomography scans in one hundred eighteen orthopaedic patients during the COVID-19 pandemic: identification of chest lesions; added values; help in managing patients; burden on the computerised tomography scan department. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 2020 Aug;44(8):1571–80. [DOI: 10.1007/s00264-020-04651-5] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Herpe 2020 {published data only}
Hwang 2020 {published data only}
Ippolito 2020 {published data only}
-
- Ippolito D, Pecorelli A, Maino C, Capodaglio C, Mariani I, Giandola T, et al.Diagnostic impact of bedside chest X-ray features of 2019 novel coronavirus in the routine admission at the emergency department: case series from Lombardy region. European Journal of Radiology 2020;129:109092. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109092] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Jalil 2020 {published data only}
Krdzalic 2020 {published data only}
Kuzan 2020 {published data only}
-
- Kuzan TY, Murzoğlu Altıntoprak K, Çiftçi HÖ, Ergül U, Ünal Özdemir NB, Bulut M, et al.A comparison of clinical, laboratory and chest CT findings of laboratory-confirmed and clinically diagnosed COVID-19 patients at first admission. Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology 2020 May;27(3):336-43. [DOI: 10.5152/dir.2020.20270] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Lieveld 2021a {published data only}
-
- Lieveld AW, Azijli K, Teunissen BP, Haaften RM, Kootte RS, van den Berk IA, et al.Chest CT in COVID-19 at the ED: validation of the COVID-19 Reporting and Data System (CO-RADS) and CT Severity Score: a prospective, multicenter, observational study. Chest 2021 Mar 1;159(3):1126-35. [DOI: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.11.026] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Lieveld 2021b {published data only}
-
- Lieveld AW, Kok B, Schuit FH, Azijli K, Heijmans J, Laarhoven A, et al.Diagnosing COVID-19 pneumonia in a pandemic setting: Lung Ultrasound versus CT (LUVCT) – a multicentre, prospective, observational study. ERJ Open Research 2020 Oct;6(4):00539-2020. [DOI: 10.1183/23120541.00539-2020] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Luo 2020a {published data only}
Majeed 2020 {published data only}
-
- Majeed T, Ali RS, Solomon J, Mesri M, Sharma S, Shamim S, et al.The role of the computed tomography (CT) thorax in the diagnosis of COVID-19 for patients presenting with acute surgical emergencies. a single institute experience. Indian Journal of Surgery 2020 Oct 20;82(6):1005-10. [DOI: 10.1007/s12262-020-02626-9] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Mei 2020 {published data only}
Miranda Magalhaes Santos 2020 {published data only}
-
- Miranda Magalhães Santos JM, Paula Alves Fonseca A, Pinheiro Zarattini Anastacio E, Formagio Minenelli F, Furtado de Albuquerque Cavalcanti C, Borges da Silva Teles G.Initial results of the use of a standardized diagnostic criteria for chest computed tomography findings in coronavirus disease 2019. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography 2020;44(5):647-51. [DOI: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000001054] - DOI - PubMed
Moroni 2021 {published data only}
Murphy 2020 {published data only}
Narinx 2020 {published data only}
Nivet 2021 {published data only}
O'Neill 2020 {published data only}
-
- O'Neill SB, Byrne D, Müller NL, Jalal S, Parker W, Nicolaou S, et al.Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) Expert consensussStatement related to chest CT findings in COVID-19 versus CO-RADS: comparison of reportingsSystem performance among chest radiologists and end-user preference. Canadian Association of Radiologists' Journal 2020;0846537120968919:Epub 2020 Nov 3. PMID: 33138634. [DOI: 10.1177/0846537120968919] - DOI - PubMed
Ohana 2021 {published data only}
-
- Ohana M, Muller J, Severac F, Bilbault P, Behr M, Oberlin M, et al.Temporal variations in the diagnostic performance of chest CT for Covid-19 depending on disease prevalence: Experience from North-Eastern France. European Journal of Radiology 2021 Jan;134:109425. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109425] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Ooi 2021 {published data only}
Pagano 2021 {published data only}
Palmisano 2021 {published data only}
Pare 2020 {published data only}
Patel 2020 {published data only}
-
- Patel M, Chowdhury J, Zheng M, Abramian O, Verga S, Zhao H, et al.High Resolution CHEST CT(HRCT) evaluation in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020;203(4). [DOI: 10.1101/2020.05.26.20114082] - DOI
Patrucco 2021 {published data only}
Peng 2020a {published data only}
-
- Peng D, Zhang J, Xu Y, Liu Z, Wu P.Clinical analysis and early differential diagnosis of suspected pediatric patients with 2019 novel coronavirus infection. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: 10.1101/2020.04.07.20057315] - DOI
Pivetta 2021 {published data only}
Puylaert 2020 {published data only}
-
- Puylaert CA Scheijmans JC, Borgstein AB, Andeweg CS, Bartels-Rutten A, Beets GL, et al.Yield of Screening for COVID-19 in asymptomatic patients prior to elective or emergency surgery using chest CT and RT-PCR (SCOUT): multicenter study. Annals of Surgery 2020 Dec;272(6):919-24. [DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000004218] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Ravikanth 2021 {published data only}
-
- Ravikanth R.Diagnostic accuracy and false-positive rate of chest CT as compared to RT-PCR in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia: a prospective cohort of 612 cases from India and review of literature. Indian Journal of Radiology & Imaging 2021 Jan;31(Suppl 1):S161-9. [DOI: 10.4103/ijri.IJRI_377_20] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Reginelli 2021 {published data only}
Rona 2021 {published data only}
Roy Choudhury 2020 {published data only}
Saeed 2020 {published data only}
Salehi‐Pourmehr 2020 {published data only}
Schalekamp 2020 {published data only}
Schmid 2020 {published data only}
-
- Schmid B, Feuerstein D, Lang CN, Fink K, Steger R, Rieder M, et al.Lung ultrasound in the emergency department - a valuable tool in the management of patients presenting with respiratory symptoms during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. BMC Emergency Medicine 2020 Dec 7;20(1):96. [DOI: 10.1186/s12873-020-00389-w] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Schulze‐hagen 2020 {published data only}
Shah 2021 {published data only}
Skalidis 2020 {published data only}
Song 2020a {published data only}
Sorlini 2021 {published data only}
Speidel 2021 {published data only}
Steuwe 2020 {published data only}
-
- Steuwe A, Rademacher C, Valentin B, Köhler M-H, Appel E, Keitel V, et al.Dose-optimised chest computed tomography for diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) - evaluation of image quality and diagnostic impact. Journal of Radiological Protection 2020;40(3):877-91. [10.1088/1361-6498/aba16a] - PubMed
Stevens 2020 {published data only}
Sukhija 2021 {published data only}
Sverzellati Nicola 2021 {published data only}
Teichgraber 2021 {published data only}
Tsakok 2020 {published data only}
Wang 2020a {published data only}
-
- Wang T, Xiong Z, Zhou H, Luo W, Tang H, Liu J.Design, validation, and clinical practice of standardized imaging diagnostic report for COVID-19. Zhong Nan da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban [Journal of Central South University Medical Sciences] 2020 Mar 28;45(3):229-35. [DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2020.200152] - DOI - PubMed
Wehbe 2021 {published data only}
Xiaocheng 2020 {published data only}
-
- Xiaocheng X, Haiyan J, Xiaoping C, Yi Z, Huiyuan S.Preliminary analysis of visits to fever clinics during the epidemic of new coronavirus pneumonia. Academic Journal of Second Military Medical University 2020;41(8):828-31. [DOI: 10.16781/j.0258‑879x.2020.08.0828] - DOI
Xiong 2020 {published data only}
Yassa 2020 {published data only}
-
- Yassa M, Yirmibes C, Cavusoglu G, Eksi H, Dogu C, Usta C, et al.Outcomes of universal SARS-CoV-2 testing program in pregnant women admitted to hospital and the adjuvant role of lung ultrasound in screening: a prospective cohort study. Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine 2020 Nov;33(22):3820-6. [DOI: 10.1080/14767058.2020.1798398] - DOI - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Ai 2020b {published data only}
-
- Ai J, Gong J, Xing L, He R, Tian F, Wang J, et al.Analysis of factors associated early diagnosis in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: 10.1101/2020.04.09.20059352] - DOI
Ai 2020c {published data only}
-
- Ai J, Chen J, Wang Y, Liu X, Fan W, Qu G, et al.The cross-sectional study of hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 patients in Xiangyang, Hubei province. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: 10.1101/2020.02.19.20025023] - DOI
Arentz 2020 {published data only}
Bai 2020a {published data only}
Bai 2020b {published data only}
Chang 2020 {published data only}
Chen 2020a {published data only}
-
- Chen S, Wu JJ, Li MZ, Xu DZ, Zhu YZ, Wang HC, et al.Clinical features of 109 cases of novel coronavirus pneumonia. Chinese Journal of Infectious Diseases 2020;38(12):E015. [DOI: 10.3760 / cma.j.issn.1000-6680.2020.0015]
Chen 2020b {published data only}
Chen 2020c {published data only}
Cheng 2020 {published data only}
-
- Cheng Z, Lu Y, Cao Q, Qin L, Pan Z, Yan F, et al.Clinical features and chest CT manifestations of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in a single-center study in Shanghai, China. American Journal of Roentgenology 2020;215(1):121-6. [DOI: 10.2214/ajr.20.22959 10.2214/AJR.20.22959.] - PubMed
Çinkooğlu 2020 {published data only}
Colombi 2020b {published data only}
Dai 2020 {published data only}
Ding 2020 {published data only}
Dong 2020 {published data only}
-
- Dong J, Wu L, Jin Q, Chen J, He J.Chest CT scan of hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a case-control study. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: 10.1101/2020.04.07.20056762] - DOI
Guan 2020 {published data only}
Hao 2020 {published data only}
Himoto 2020 {published data only}
Huang 2020 {published data only}
Liang 2020 {published data only}
-
- Liang Y, Liang J, Zhou Q, Li X, Lin F, Deng Z, et al.Prevalence and clinical features of 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in the Fever Clinic of a teaching hospital in Beijing: a single-center, retrospective study. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: 10.1101/2020.02.25.20027763] - DOI
Lu 2020 {published data only}
Mao 2020 {published data only}
Miao 2020a {published data only}
-
- Miao C, Zhuang J, Jin M, Xiong H, Huang P, Zhao Q, et al.A comparative multi-centre study on the clinical and imaging features of confirmed and unconfirmed patients with COVID-19. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: 10.1101/2020.03.22.20040782] - DOI
Miao 2020b {published data only}
Pakray 2020 {published data only}
Poggiali 2020 {published data only}
Pu 2020 {published data only}
Siegel 2020 {published data only}
Song 2020b {published data only}
Tavare 2020 {published data only}
Wang 2020b {published data only}
Wu 2020a {published data only}
-
- Wu J, Feng CL, Xian XY, Qiang J, Zhang J, Mao QX, et al.Novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) CT distribution and sign features. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases] 2020;43(4):321-6. [DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20200217-00106 10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20200217-00106.] - PubMed
Wu 2020b {published data only}
-
- Wu Q, Xing Y, Shi L, Li W, Gao Y, Pan S, et al.Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of children with coronavirus disease 2019. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: 10.1101/2020.03.19.20027078] - DOI
Wu 2020c {published data only}
Wu 2020d {published data only}
Xie 2020 {published data only}
Xu 2020a {published data only}
Xu 2020b {published data only}
Yang 2020a {published data only}
Yang 2020b {published data only}
Yuan 2020 {published data only}
Additional references
Bossuyt 2015
BSTI 2020
-
- British Society of Thoracic Imaging.COVID-19 BSTI Reporting Templates and Codes. bsti.org.uk/covid-19-resources/covid-19-bsti-reporting-templates/ 2020 (accessed 4 January 2020).
Butler‐Laporte 2021
-
- Butler-Laporte G, Lawandi A, Schiller I, Yao MC, Dendukuri N, McDonald E, et al.Comparison of saliva and nasopharyngeal swab nucleic acid amplification testing for detection of SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Internal Medicine 2021;18(3):353-60. [DOI: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.8876] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
China National Health Comission 2020
-
- China National Health Comission.Chinese Clinical Guidance for COVID-19 Pneumonia Diagnosis and Treatment (7th Edition). kjfy.meetingchina.org/msite/news/show/cn/3337.html 2020 (accessed 24 January 2020).
Chu 2006
Datta 2020
Deeks 2020
Dinnes 2020
Dinnes 2021
Han 2020
Harbord 2009
-
- Harbord RM, Whiting P.metandi: meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy using hierarchical logistic regression. Stata Journal 2009;9(2):211-29. [DOI: 10.1177/1536867X0900900203] - DOI
Hong 2018
Irwig 1995
Kanne 2020
Korevaar 2020
Kucirka 2020
Lee 2020
Leeflang 2021
-
- Leeflang MMG, Bell K, Deeks JJ, Dinnes J, Doust J, Korevaar DA, et al.Electronic and animal noses for detecting SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2021 Jun 28, Issue 6. Art. No: CD015013. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD015013] - DOI
Li 2020a
Li 2020b
Loeffelholz 2020
McGrath 2017
Moher 2009
Ng 2020
Pan 2020
Pedersen 2020
-
- Pedersen, TL.Package ‘ggforce’. www.ggforce.data-imaginist.com 2020 (accessed 5 January 2020).
Peng 2020b
Prokop 2020
R Core Team 2021 [Computer program]
-
- R: A language and environment for statistical computing.R Core Team. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing, 2020.
Reitsma 2005
Rubin 2020
-
- Rubin GD, Ryerson CJ, Haramati LB, Sverzellati N, Kanne JP, Raoof S, et al.The role of chest imaging in patient management during the COVID-19 pandemic: a multinational consensus statement from the Fleischner Society. Radiology 2020;296(1):172–80. [DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2020201365] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Salameh 2020b
Salehi 2020
Shi 2020
Simpson 2020
-
- Simpson S, Kay FU, Abbara S, Bhalla S, Chung JH, Chung M, et al.Radiological Society of North America expert consensus document on reporting chest CT findings related to COVID-19: endorsed by the Society of Thoracic Radiology, the American College of Radiology, and RSNA. Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging 2020;2(2):e200152. [DOI: 10.1148/ryct.2020200152] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Soldati 2020
-
- Soldati G, Smargiassi A, Inchingolo R, Buonsenso D, Perrone T, Briganti DF, et al.Proposal for international Ssandardization of the use oflLung ultrasound for patients with COVID-19: a simple, quantitative, reproducible method. Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine 2020 Jul;39(7):1413-9. [DOI: 10.1002/jum.15285] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
StataCorp 2019 [Computer program]
-
- Stata Statistical Software.StataCorp, Version Release 16. College Station, TX: StataCorp LLC, 2019.
Stegeman 2020
Struyf 2020
-
- Struyf T, Deeks JJ, Dinnes J, Takwoingi Y, Davenport C, Leeflang MM, et al.Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19 disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2020, Issue 7. Art. No: CD013665. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Walker 2020
-
- Walker M.What does asymptomatic COVID-19 look like under the surface? www.medpagetoday.com/infectiousdisease/covid19/87168 2020 (accessed 25 July 2021).
WHO 2020
-
- World Health Organization (WHO).WHO COVID-19 Case definition. WHO/2019-nCoV/Surveillance_Case_Definition/2020.1 2020 (accessed 17 October 2020).
Wickham 2016
-
- Wickham H.ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis. New York: Springer-Verlag, 2016.
Ye 2020
Zhang 2020
Zhao 2020
References to other published versions of this review
Islam 2020
Islam 2021
McInnes 2020
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

