Development of the Quantum-Inspired SIBFA Many-Body Polarizable Force Field: Enabling Condensed-Phase Molecular Dynamics Simulations
- PMID: 35575306
- PMCID: PMC10851344
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jctc.2c00029
Development of the Quantum-Inspired SIBFA Many-Body Polarizable Force Field: Enabling Condensed-Phase Molecular Dynamics Simulations
Abstract
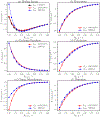
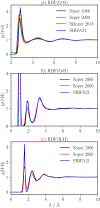
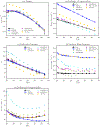
We present the extension of the Sum of Interactions Between Fragments Ab initio Computed (SIBFA) many-body polarizable force field to condensed-phase molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. The quantum-inspired SIBFA procedure is grounded on simplified integrals obtained from localized molecular orbital theory and achieves full separability of its intermolecular potential. It embodies long-range multipolar electrostatics (up to quadrupole) coupled to a short-range penetration correction (up to charge-quadrupole), exchange repulsion, many-body polarization, many-body charge transfer/delocalization, exchange dispersion, and dispersion (up to C10). This enables the reproduction of all energy contributions of ab initio symmetry-adapted perturbation theory (SAPT(DFT)) gas-phase reference computations. The SIBFA approach has been integrated within the Tinker-HP massively parallel MD package. To do so, all SIBFA energy gradients have been derived and the approach has been extended to enable periodic boundary conditions simulations using smooth particle mesh Ewald. This novel implementation also notably includes a computationally tractable simplification of the many-body charge transfer/delocalization contribution. As a proof of concept, we perform a first computational experiment defining a water model fitted on a limited set of SAPT(DFT) data. SIBFA is shown to enable a satisfactory reproduction of both gas-phase energetic contributions and condensed-phase properties highlighting the importance of its physically motivated functional form.
Figures
References
-
- Stone A The theory of intermolecular forces; Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK., 2013.
-
- Warshel A; Kato M; Pisliakov AV Polarizable Force Fields: History, Test Cases, and Prospects. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation 2007, 3, 2034–2045, - PubMed
-
- Shi Y; Ren P; Schnieders M; Piquemal J-P Reviews in Computational Chemistry Volume 28; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2015; Chapter 2, pp 51–86.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
