The WalRK Two-Component System Is Essential for Proper Cell Envelope Biogenesis in Clostridioides difficile
- PMID: 35575581
- PMCID: PMC9210968
- DOI: 10.1128/jb.00121-22
The WalRK Two-Component System Is Essential for Proper Cell Envelope Biogenesis in Clostridioides difficile
Abstract
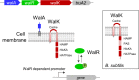
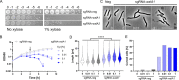
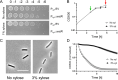
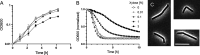
The WalR-WalK two-component regulatory system (TCS) is found in all Firmicutes, in which it regulates the expression of multiple genes required for remodeling the cell envelope during growth and division. Unlike most TCSs, WalRK is essential for viability, so it has attracted interest as a potential antibiotic target. In this study, we used overexpression of WalR and CRISPR interference to investigate the Wal system of Clostridioides difficile, a major cause of hospital-associated diarrhea in high-income countries. We confirmed that the wal operon is essential and identified morphological defects and cell lysis as the major terminal phenotypes of altered wal expression. We also used transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) to identify over 150 genes whose expression changes in response to WalR levels. This gene set is enriched in cell envelope genes and includes genes encoding several predicted PG hydrolases and proteins that could regulate PG hydrolase activity. A distinct feature of the C. difficile cell envelope is the presence of an S-layer, and we found that WalR affects expression of several genes which encode S-layer proteins. An unexpected finding was that some Wal-associated phenotypic defects were inverted in comparison to what has been reported for other Firmicutes. For example, downregulation of Wal signaling caused C. difficile cells to become longer rather than shorter, as in Bacillus subtilis. Likewise, downregulation of Wal rendered C. difficile more sensitive to vancomycin, whereas reduced Wal activity is linked to increased vancomycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. IMPORTANCE The WalRK two-component system (TCS) is essential for coordinating synthesis and turnover of peptidoglycan in Firmicutes. We investigated the WalRK TCS in Clostridioides difficile, an important bacterial pathogen with an atypical cell envelope. We confirmed that WalRK is essential and regulates cell envelope biogenesis, although several of the phenotypic changes we observed were opposite to what has been reported for other Firmicutes. We also identified over 150 genes whose expression is controlled either directly or indirectly by WalR. Overall, our findings provide a foundation for future investigations of an important regulatory system and potential antibiotic target in C. difficile.
Keywords: cell envelope; regulation of gene expression; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Xylose-Inducible Expression System and a CRISPR Interference Plasmid for Targeted Knockdown of Gene Expression in Clostridioides difficile.J Bacteriol. 2019 Jun 21;201(14):e00711-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00711-18. Print 2019 Jul 15. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30745377 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of DraRS in Clostridioides difficile, a Two-Component Regulatory System That Responds to Lipid II-Interacting Antibiotics.J Bacteriol. 2023 Oct 26;205(10):e0016423. doi: 10.1128/jb.00164-23. Epub 2023 Jul 13. J Bacteriol. 2023. PMID: 37439672 Free PMC article.
-
Ser/Thr Kinase-Dependent Phosphorylation of the Peptidoglycan Hydrolase CwlA Controls Its Export and Modulates Cell Division in Clostridioides difficile.mBio. 2021 May 18;12(3):e00519-21. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00519-21. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34006648 Free PMC article.
-
A matter of life and death: cell wall homeostasis and the WalKR (YycGF) essential signal transduction pathway.Mol Microbiol. 2008 Dec;70(6):1307-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06483.x. Epub 2008 Oct 23. Mol Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 19019149 Review.
-
Tearing down the wall: peptidoglycan metabolism and the WalK/WalR (YycG/YycF) essential two-component system.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;631:214-28. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-78885-2_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18792692 Review.
Cited by
-
A sequence invariable region in TcdB2 is required for toxin escape from Clostridioides difficile.J Bacteriol. 2024 Jul 25;206(7):e0009624. doi: 10.1128/jb.00096-24. Epub 2024 Jun 18. J Bacteriol. 2024. PMID: 38888328 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding our grasp of two-component signaling in Clostridioides difficile.J Bacteriol. 2023 Oct 26;205(10):e0018823. doi: 10.1128/jb.00188-23. Epub 2023 Sep 20. J Bacteriol. 2023. PMID: 37728603 Free PMC article.
-
Butyrate enhances Clostridioides difficile sporulation in vitro.J Bacteriol. 2023 Sep 26;205(9):e0013823. doi: 10.1128/jb.00138-23. Epub 2023 Sep 1. J Bacteriol. 2023. PMID: 37655912 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Essential Genes in Clostridioides difficile by CRISPRi and Tn-seq.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 9:2025.06.04.657922. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.04.657922. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40502013 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
HexSDF Is Required for Synthesis of a Novel Glycolipid That Mediates Daptomycin and Bacitracin Resistance in C. difficile.mBio. 2023 Apr 25;14(2):e0339722. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03397-22. Epub 2023 Feb 14. mBio. 2023. PMID: 36786594 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dubrac S, Boneca IG, Poupel O, Msadek T. 2007. New insights into the WalK/WalR (YycG/YycF) essential signal transduction pathway reveal a major role in controlling cell wall metabolism and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 189:8257–8269. 10.1128/JB.00645-07. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

