Measurement of 7-dehydrocholesterol and cholesterol in hair can be used in the diagnosis of Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome
- PMID: 35577137
- PMCID: PMC9207299
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jlr.2022.100228
Measurement of 7-dehydrocholesterol and cholesterol in hair can be used in the diagnosis of Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome
Abstract
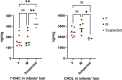
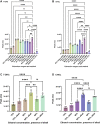
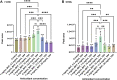
7-dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC) and cholesterol (CHOL) are biomarkers of Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome (SLOS), a congenital autosomal recessive disorder characterized by elevated 7-DHC level in patients. Hair samples have been shown to have great diagnostic and research value, which has long been neglected in the SLOS field. In this study, we sought to investigate the feasibility of using hair for SLOS diagnosis. In the presence of antioxidants (2,6-ditert-butyl-4-methylphenol and triphenylphosphine), hair samples were completely pulverized and extracted by micro-pulverized extraction in alkaline solution or in n-hexane. After microwave-assisted derivatization with N,O-Bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide, the analytes were measured by GC-MS. We found that the limits of determination for 7-DHC and CHOL were 10 ng/mg and 8 ng/mg, respectively. In addition, good linearity was obtained in the range of 50-4000 ng/mg and 30-6000 ng/mg for 7-DHC and CHOL, respectively, which fully meets the requirement for SLOS diagnosis and related research. Finally, by applying the proposed method to real hair samples collected from 14 healthy infants and two suspected SLOS patients, we confirmed the feasibility of hair analysis as a diagnostic tool for SLOS. In conclusion, we present an optimized and validated analytical method for the simultaneous determination of two SLOS biomarkers using human hair.
Keywords: diagnostic test; gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; hair analysis; micro-pulverized extraction; microwave-assisted derivatization.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Schade D.S., Shey L., Eaton R.P. Cholesterol review: a metabolically important molecule. Endocr. Pract. 2020;26:1514–1523. - PubMed
-
- Kelley R.I. Diagnosis of Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry of 7-dehydrocholesterol in plasma, amniotic fluid and cultured skin fibroblasts. Clin. Chim. Acta. 1995;236:45–58. - PubMed
-
- Smith D.W., Lemli L., Opitz J.M. A newly recognized syndrome of multiple congenital anomalies. J. Pediatr. 1964;64:210–217. - PubMed
-
- Porter F.D. Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome: pathogenesis, diagnosis and management. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2008;16:535–541. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

