Efficacy of tofacitinib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis stratified by baseline body mass index: an analysis of pooled data from phase 3 studies
- PMID: 35577477
- PMCID: PMC9114845
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-002103
Efficacy of tofacitinib in patients with rheumatoid arthritis stratified by baseline body mass index: an analysis of pooled data from phase 3 studies
Abstract
Objective: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This post hoc analysis assessed whether baseline body mass index (BMI) impacts tofacitinib efficacy in patients with RA.
Methods: Pooled data from six phase 3 studies in patients receiving tofacitinib 5 mg (N=1589) or 10 mg (N=1611) twice daily or placebo (advancing to active treatment at months 3 or 6; N=680), ±conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, were stratified by baseline BMI (<25, 25 to <30, ≥30 kg/m2). Endpoints (through to month 6) were assessed descriptively: American College of Rheumatology 20/50/70 response rates; changes from baseline (∆) in Disease Activity Score in 28 joints, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-4(ESR)), DAS28-4(C-reactive protein), Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI), Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI) and pain; and proportions of patients achieving DAS28-4(ESR) ≥1.2 and HAQ-DI ≥0.22 decreases from baseline, low disease activity (DAS28-4(ESR) ≤3.2 or CDAI ≤10) and radiographic non-progression (Δmodified Total Sharp Score ≤0.5; months 12 and 24). Estimates were adjusted using multivariable models for selected outcomes. Univariate/multivariable regression analyses determined predictors of month 6 outcomes.
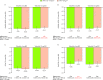
Results: Of 3880 patients included, 1690 (43.6%), 1173 (30.2%) and 1017 (26.2%) had baseline BMI <25, 25 to <30 and ≥30 kg/m2, respectively. Tofacitinib showed greater efficacy improvements versus placebo in each BMI category. Differences in efficacy outcomes (adjusted and unadjusted) were generally not clinically meaningful across BMI categories within treatment groups. In regression analyses, BMI was not consistently associated with selected outcomes.
Conclusions: Baseline BMI did not consistently affect tofacitinib response suggesting that tofacitinib is an effective oral treatment option for adults with moderate to severe RA regardless of baseline BMI, including patients with BMI ≥30 kg/m2.
Trial registration numbers: NCT00814307, NCT01039688; NCT00960440; NCT00847613; NCT00856544; NCT00853385.
Keywords: antirheumatic agents; arthritis, rheumatoid; therapeutics.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: AHD has received consulting fees or other remuneration from AbbVie, Crescendo, Gilead, Mallinckrodt, Pfizer Inc, Regeneron and Sanofi-Genzyme, and is on the speakers bureau for AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Crescendo, Genentech, Eli Lilly, Mallinckrodt, Pfizer Inc, and Sanofi-Genzyme. MAG-G has received grants/research support from AbbVie, MSD and Roche, and has received consultation fees/participation in company-sponsored speakers bureau from AbbVie, Celgene, MSD, Pfizer Inc, Roche and Sanofi. FW has received research grants from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Genzyme, Pfizer Inc, Regeneron, and Sanofi, has received consulting fees or other remuneration from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genzyme, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, Regeneron, and Sanofi, and is on the speakers bureau for AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genzyme, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, Regeneron, and Sanofi. JMAG has received consulting or speaking fees from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, MSD, Pfizer Inc, Roche and UCB. LT, LS, HS and ST are employees and shareholders of Pfizer Inc. JP is an employee of Syneos Health, who were paid contractors to Pfizer Inc in the development of this manuscript and for the provision of statistical support. JRC has received research grants from Amgen, Corrona, Crescendo Bio, and Pfizer Inc, and has received consulting fees or other remuneration from AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Corrona, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Myriad, Pfizer Inc, Roche/Genentech and UCB.
Figures

References
-
- Fleischmann R, Cutolo M, Genovese MC, et al. . Phase IIb dose-ranging study of the oral JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (CP-690,550) or adalimumab monotherapy versus placebo in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Arthritis Rheum 2012;64:617–29. 10.1002/art.33383 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kremer JM, Cohen S, Wilkinson BE, et al. . A phase IIb dose-ranging study of the oral JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (CP-690,550) versus placebo in combination with background methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate alone. Arthritis Rheum 2012;64:970–81. 10.1002/art.33419 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kremer JM, Bloom BJ, Breedveld FC, et al. . The safety and efficacy of a JAK inhibitor in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled phase IIA trial of three dosage levels of CP-690,550 versus placebo. Arthritis Rheum 2009;60:1895–905. 10.1002/art.24567 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
