Modelling chronic pancreatitis as a complex genetic disease in mice
- PMID: 35577534
- PMCID: PMC9666703
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2022-327601
Modelling chronic pancreatitis as a complex genetic disease in mice
Keywords: ACUTE PANCREATITIS; CHRONIC PANCREATITIS; PANCREATIC DISORDERS; TRYPSINOGEN.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
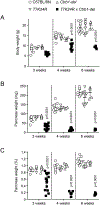

Comment on
-
Novel p.K374E variant of CPA1 causes misfolding-induced hereditary pancreatitis with autosomal dominant inheritance.Gut. 2020 Apr;69(4):790-792. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318751. Epub 2019 Apr 20. Gut. 2020. PMID: 31005883 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Heterozygous Spink1 c.194+2T>C mutant mice spontaneously develop chronic pancreatitis.Gut. 2020 May;69(5):967-968. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318790. Epub 2019 May 29. Gut. 2020. PMID: 31142585 No abstract available.
-
NGS mismapping confounds the clinical interpretation of the PRSS1 p.Ala16Val (c.47C>T) variant in chronic pancreatitis.Gut. 2022 Apr;71(4):841-842. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2021-324943. Epub 2021 May 7. Gut. 2022. PMID: 33963039 No abstract available.
-
Alcohol amplifies the association between common variants at PRSS1-PRSS2 locus and chronic pancreatitis in a dose-dependent manner.Gut. 2022 Nov;71(11):2369-2371. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2021-326670. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Gut. 2022. PMID: 34996825 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wang YC, Mao XT, Yu D, Mao SH, Li ZS, Zou WB, Liao Z. Alcohol amplifies the association between common variants at PRSS1-PRSS2 locus and chronic pancreatitis in a dose-dependent manner. Gut 2022. Jan 7. gutjnl-2021-326670 - PubMed
-
- Génin E, Cooper DN, Masson E, Férec C, Chen JM. NGS mismapping confounds the clinical interpretation of the PRSS1 p.Ala16Val (c.47C>T) variant in chronic pancreatitis. Gut 2022, 71:841–842 - PubMed
-
- Sun C, Liu M, An W, Mao X, Jiang H, Zou W, Wu H, Liao Z, Li Z. Heterozygous Spink1 c.194+2T>C mutant mice spontaneously develop chronic pancreatitis. Gut 2020, 69:967–968 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
