Arginase-1 Is Required for Macrophage-Mediated Renal Tubule Regeneration
- PMID: 35577558
- PMCID: PMC9161787
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2021121548
Arginase-1 Is Required for Macrophage-Mediated Renal Tubule Regeneration
Abstract
Background: After kidney injury, macrophages transition from initial proinflammatory activation to a proreparative phenotype characterized by expression of arginase-1 (Arg1), mannose receptor 1 (Mrc1), and macrophage scavenger receptor 1 (Msr1). The mechanism by which these alternatively activated macrophages promote repair is unknown.
Methods: We characterized the macrophage and renal responses after ischemia-reperfusion injury with contralateral nephrectomy in LysM-Cre;Arg1fl/fl mice and littermate controls and used in vitro coculture of macrophages and tubular cells to determine how macrophage-expressed arginase-1 promotes kidney repair.
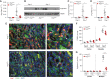
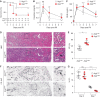
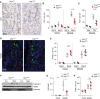
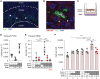
Results: After ischemia-reperfusion injury with contralateral nephrectomy, Arg1-expressing macrophages were almost exclusively located in the outer stripe of the medulla adjacent to injured S3 tubule segments containing luminal debris or casts. Macrophage Arg1 expression was reduced by more than 90% in injured LysM-Cre;Arg1fl/fl mice, resulting in decreased mouse survival, decreased renal tubular cell proliferation and decreased renal repair compared with littermate controls. In vitro studies demonstrate that tubular cells exposed apically to dead cell debris secrete high levels of GM-CSF and induce reparative macrophage activation, with those macrophages in turn secreting Arg1-dependent factor(s) that directly stimulate tubular cell proliferation.
Conclusions: GM-CSF-induced, proreparative macrophages express arginase-1, which is required for the S3 tubular cell proliferative response that promotes renal repair after ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Keywords: arginase-1; kidney repair; kidney tubules; macrophage; regeneration.
Copyright © 2022 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
Comment in
-
More than a Marker: Arginase-1 in Kidney Repair.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022 Jun;33(6):1051-1053. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2022020161. Epub 2022 May 16. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35577557 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Most Arginase-1 Positive Cells Are Likely Injured S3 Proximal Tubular Cells Carrying Upregulated Phagocytotic Capacity rather than M2 Macrophages-Too Many To Be True.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022 Nov;33(11):2123-2124. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2022070761. Epub 2022 Sep 9. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 36316093 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Authors' Reply: Most Arginase-1 Positive Cells Are Likely Injured S3 Proximal Tubular Cells Carrying Upregulated Phagocytotic Capacity rather than M2 Macrophages-Too Many To Be True.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022 Nov;33(11):2124-2125. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2022070836. Epub 2022 Sep 9. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 36316094 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Day YJ, Huang L, Ye H, Linden J, Okusa MD: Renal ischemia-reperfusion injury and adenosine 2A receptor-mediated tissue protection: Role of macrophages. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 288: F722–F731, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Jo SK, Sung SA, Cho WY, Go KJ, Kim HK: Macrophages contribute to the initiation of ischaemic acute renal failure in rats. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21: 1231–1239, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

