Antimicrobial properties of chitosan from different developmental stages of the bioconverter insect Hermetia illucens
- PMID: 35577828
- PMCID: PMC9110362
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-12150-3
Antimicrobial properties of chitosan from different developmental stages of the bioconverter insect Hermetia illucens
Abstract
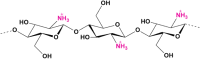
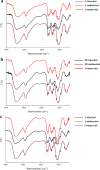
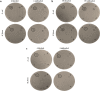
Growing antimicrobial resistance has prompted researchers to identify new natural molecules with antimicrobial potential. In this perspective, attention has been focused on biopolymers that could also be functional in the medical field. Chitin is the second most abundant biopolymer on Earth and with its deacetylated derivative, chitosan, has several applications in biomedical and pharmaceutical fields. Currently, the main source of chitin is the crustacean exoskeleton, but the growing demand for these polymers on the market has led to search for alternative sources. Among these, insects, and in particular the bioconverter Hermetia illucens, is one of the most bred. Chitin can be extracted from larvae, pupal exuviae and dead adults of H. illucens, by applying chemical methods, and converted into chitosan. Fourier-transformed infrared spectroscopy confirmed the identity of the chitosan produced from H. illucens and its structural similarity to commercial polymer. Recently, studies showed that chitosan has intrinsic antimicrobial activity. This is the first research that investigated the antibacterial activity of chitosan produced from the three developmental stages of H. illucens through qualitative and quantitative analysis, agar diffusion tests and microdilution assays, respectively. Our results showed the antimicrobial capacity of chitosan of H. illucens, opening new perspectives for its use in the biological area.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Dossey, A. T., Tatum, J. T., & McGill, W. L. Modern insect-based food industry: current status, insect processing technology, and recommendations moving forward. In Insects as sustainable food ingredients. 113–152 (Academic Press, 2016).
-
- Van Huis A. Insects as food and feed, a new emerging agricultural sector: a review. J. Insects Food Feed. 2020;6(1):27–44. doi: 10.3920/JIFF2019.0017. - DOI
-
- Derrien, C., & Boccuni, A. Current status of the insect producing industry in Europe. In Edible insects in sustainable food systems 471–479 (Springer. 2018).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

