Glaucoma diagnosis using multi-feature analysis and a deep learning technique
- PMID: 35577876
- PMCID: PMC9110703
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-12147-y
Glaucoma diagnosis using multi-feature analysis and a deep learning technique
Abstract
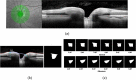
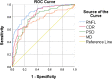
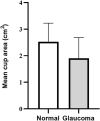
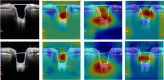
In this study, we aimed to facilitate the current diagnostic assessment of glaucoma by analyzing multiple features and introducing a new cross-sectional optic nerve head (ONH) feature from optical coherence tomography (OCT) images. The data (n = 100 for both glaucoma and control) were collected based on structural, functional, demographic and risk factors. The features were statistically analyzed, and the most significant four features were used to train machine learning (ML) algorithms. Two ML algorithms: deep learning (DL) and logistic regression (LR) were compared in terms of the classification accuracy for automated glaucoma detection. The performance of the ML models was evaluated on unseen test data, n = 55. An image segmentation pilot study was then performed on cross-sectional OCT scans. The ONH cup area was extracted, analyzed, and a new DL model was trained for glaucoma prediction. The DL model was estimated using five-fold cross-validation and compared with two pre-trained models. The DL model trained from the optimal features achieved significantly higher diagnostic performance (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) 0.98 and accuracy of 97% on validation data and 96% on test data) compared to previous studies for automated glaucoma detection. The second DL model used in the pilot study also showed promising outcomes (AUC 0.99 and accuracy of 98.6%) to detect glaucoma compared to two pre-trained models. In combination, the result of the two studies strongly suggests the four features and the cross-sectional ONH cup area trained using deep learning have a great potential for use as an initial screening tool for glaucoma which will assist clinicians in making a precise decision.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Al-Aswad LA. Glaucoma Today. Bryn Mawr Communications; 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

