A comprehensive SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 review, Part 1: Intracellular overdrive for SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 35577935
- PMCID: PMC9108708
- DOI: 10.1038/s41431-022-01108-8
A comprehensive SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 review, Part 1: Intracellular overdrive for SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
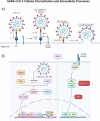
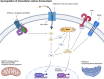
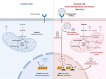
COVID-19, the disease caused by SARS-CoV-2, has claimed approximately 5 million lives and 257 million cases reported globally. This virus and disease have significantly affected people worldwide, whether directly and/or indirectly, with a virulent pathogen that continues to evolve as we race to learn how to prevent, control, or cure COVID-19. The focus of this review is on the SARS-CoV-2 virus' mechanism of infection and its proclivity at adapting and restructuring the intracellular environment to support viral replication. We highlight current knowledge and how scientific communities with expertize in viral, cellular, and clinical biology have contributed to increase our understanding of SARS-CoV-2, and how these findings may help explain the widely varied clinical observations of COVID-19 patients.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

