TP53, CDKN2A/P16, and NFE2L2/NRF2 regulate the incidence of pure- and combined-small cell lung cancer in mice
- PMID: 35577980
- PMCID: PMC10039451
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-022-02348-0
TP53, CDKN2A/P16, and NFE2L2/NRF2 regulate the incidence of pure- and combined-small cell lung cancer in mice
Erratum in
-
Correction: TP53, CDKN2A/P16, and NFE2L2/NRF2 regulate the incidence of pure- and combined-small cell lung cancer in mice.Oncogene. 2022 Sep;41(39):4485. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02442-3. Oncogene. 2022. PMID: 36002660 No abstract available.
Abstract
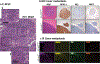
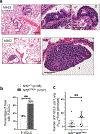
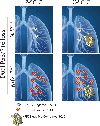
Studies have shown that Nrf2E79Q/+ is one of the most common mutations found in human tumors. To elucidate how this genetic change contributes to lung cancer, we compared lung tumor development in a genetically-engineered mouse model (GEMM) with dual Trp53/p16 loss, the most common mutations found in human lung tumors, in the presence or absence of Nrf2E79Q/+. Trp53/p16-deficient mice developed combined-small cell lung cancer (C-SCLC), a mixture of pure-SCLC (P-SCLC) and large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma. Mice possessing the LSL-Nrf2E79Q mutation showed no difference in the incidence or latency of C-SCLC compared with Nrf2+/+ mice. However, these tumors did not express NRF2 despite Cre-induced recombination of the LSL-Nrf2E79Q allele. Trp53/p16-deficient mice also developed P-SCLC, where activation of the NRF2E79Q mutation associated with a higher incidence of this tumor type. All C-SCLCs and P-SCLCs were positive for NE-markers, NKX1-2 (a lung cancer marker) and negative for P63 (a squamous cell marker), while only P-SCLC expressed NRF2 by immunohistochemistry. Analysis of a consensus NRF2 pathway signature in human NE+-lung tumors showed variable activation of NRF2 signaling. Our study characterizes the first GEMM that develops C-SCLC, a poorly-studied human cancer and implicates a role for NRF2 activation in SCLC development.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest to report
Figures



Similar articles
-
A conditional mouse expressing an activating mutation in NRF2 displays hyperplasia of the upper gastrointestinal tract and decreased white adipose tissue.J Pathol. 2020 Oct;252(2):125-137. doi: 10.1002/path.5504. Epub 2020 Aug 29. J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32619021 Free PMC article.
-
The expression of YAP1 and other transcription factors contributes to lineage plasticity in combined small cell lung carcinoma.J Pathol Clin Res. 2024 Sep;10(5):e70001. doi: 10.1002/2056-4538.70001. J Pathol Clin Res. 2024. PMID: 39283755 Free PMC article.
-
NRF2 Activation in Trp53;p16-deficient Mice Drives Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cancer Res Commun. 2024 Feb 21;4(2):487-495. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-23-0386. Cancer Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38335300 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular genetics of small cell lung carcinoma.Semin Oncol. 2001 Apr;28(2 Suppl 4):3-13. Semin Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11479891 Review.
-
Molecular Subtypes of High-Grade Neuroendocrine Carcinoma (HGNEC): What is YAP1-Positive HGNEC?Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Mar 19;27(3):108. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2703108. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 35345340 Review.
Cited by
-
The Multi-Faceted Consequences of NRF2 Activation throughout Carcinogenesis.Mol Cells. 2023 Mar 31;46(3):176-186. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2023.2191. Epub 2023 Mar 22. Mol Cells. 2023. PMID: 36994476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YAP1 Status Defines Two Intrinsic Subtypes of LCNEC with Distinct Molecular Features and Therapeutic Vulnerabilities.Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Oct 15;30(20):4743-4754. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-0361. Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39150543
-
Distinct Nrf2 Signaling Thresholds Mediate Lung Tumor Initiation and Progression.Cancer Res. 2023 Jun 15;83(12):1953-1967. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-3848. Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37062029 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modifications in early stage lung cancer: pathogenesis, biomarkers, and early diagnosis.MedComm (2020). 2025 Feb 21;6(3):e70080. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70080. eCollection 2025 Mar. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 39991629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of Genetic Mutations on the Efficacy of Immunotherapies in Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 7;25(22):11954. doi: 10.3390/ijms252211954. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596025 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 2020; 70: 7–30. - PubMed
-
- Society AC. Cancer Facts and Figures 2019. American Cancer Society Inc., 2019.
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin 2019; 69: 7–34. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S, Greulich H, Gabriel S et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 2004; 304: 1497–1500. - PubMed
-
- Kodama T, Tsukaguchi T, Satoh Y, Yoshida M, Watanabe Y, Kondoh O et al. Alectinib shows potent antitumor activity against RET-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 2014; 13: 2910–2918. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

