Lighting Up Neural Circuits by Viral Tracing
- PMID: 35578093
- PMCID: PMC9672192
- DOI: 10.1007/s12264-022-00860-7
Lighting Up Neural Circuits by Viral Tracing
Abstract
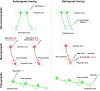
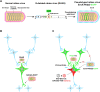
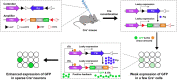
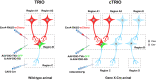
Neurons are highly interwoven to form intricate neural circuits that underlie the diverse functions of the brain. Dissecting the anatomical organization of neural circuits is key to deciphering how the brain processes information, produces thoughts, and instructs behaviors. Over the past decades, recombinant viral vectors have become the most commonly used tracing tools to define circuit architecture. In this review, we introduce the current categories of viral tools and their proper application in circuit tracing. We further discuss some advances in viral tracing strategy and prospective innovations of viral tools for future study.
Keywords: Anterograde; Neural circuit; Retrograde; Transsynaptic; Viral tracing.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors claim that there are no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kristensson K, Olsson Y. Uptake and retrograde axonal transport of peroxidase in hypoglossal neurones. Acta Neuropathol. 1971;19:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Kristensson K, Olsson Y. Retrograde axonal transport of protein. Brain Res. 1971;29:363–365. - PubMed
-
- Gerfen CR, Sawchenko PE. An anterograde neuroanatomical tracing method that shows the detailed morphology of neurons, their axons and terminals: Immunohistochemical localization of an axonally transported plant lectin, Phaseolus vulgaris-leucoagglutinin (PHA-L) Brain Res. 1984;290:219–238. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Glover JC, Petursdottir G, Jansen JK. Fluorescent dextran-amines used as axonal tracers in the nervous system of the chicken embryo. J Neurosci Methods. 1986;18:243–254. - PubMed
-
- Schmued LC, Fallon JH. Fluoro-Gold: a new fluorescent retrograde axonal tracer with numerous unique properties. Brain Res. 1986;377:147–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

