Identification and validation of an eight-lncRNA signature that predicts prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 35578166
- PMCID: PMC9109328
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-022-00331-x
Identification and validation of an eight-lncRNA signature that predicts prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is correlated with worse clinical prognosis and lacks available targeted therapy. Thus, identification of reliable biomarkers is required for the diagnosis and treatment of ESCC.
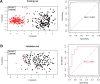
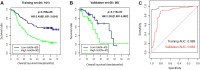
Methods: We downloaded the GSE53625 dataset as a training dataset to screen differentially expressed RNAs (DERs) with the criterion of false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05 and |log2fold change (FC)| > 1. A support vector machine classifier was used to find the optimal feature gene set that could conclusively distinguish different samples. An eight-lncRNA signature was identified by random survival forest algorithm and multivariate Cox regression analysis. The RNA sequencing data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database were used for external validation. The predictive value of the signature was assessed using Kaplan-Meier test, time-dependent receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, and dynamic area under the curve (AUC). Furthermore, a nomogram to predict patients' 3-year and 5-year prognosis was constructed. CCK-8 assay, flow cytometry, and transwell assay were conducted in ESCC cells.
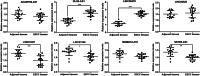
Results: A total of 1136 DERs, including 689 downregulated mRNAs, 318 upregulated mRNAs, 74 downregulated lncRNAs and 55 upregulated lncRNAs, were obtained in the GES53625 dataset. From the training dataset, we identified an eight-lncRNA signature, (ADAMTS9-AS1, DLX6-AS1, LINC00470, LINC00520, LINC01497, LINC01749, MAMDC2-AS1, and SSTR5-AS1). A nomogram based on the eight-lncRNA signature, age, and pathologic stage was developed and showed good accuracy for predicting 3-year and 5-year survival probability of patients with ESCC. Functionally, knockdown of LINC00470 significantly suppressed cell proliferation, G1/S transition, and migration in two ESCC cell lines (EC9706 and TE-9). Moreover, knockdown of LINC00470 downregulated the protein levels of PCNA, CDK4, and N-cadherin, while upregulating E-cadherin protein level in EC9706 and TE-9 cells.
Conclusion: Our eight-lncRNA signature and nomogram can provide theoretical guidance for further research on the molecular mechanism of ESCC and the screening of molecular markers.
Keywords: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; Long noncoding RNA; Nomogram; Signature.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Arnold M, Soerjomataram I, Ferlay J, Forman D. Global incidence of oesophageal cancer by histological subtype in 2012. Gut. 2015;64(3):381–387. - PubMed
-
- Herszenyi L, Tulassay Z. Epidemiology of gastrointestinal and liver tumors. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2010;14(4):249–258. - PubMed
-
- Aquino JL, Said MM, Pereira DA, Cecchino GN, Leandro-Merhi VA. Complications of the rescue esophagectomy in advanced esophageal cancer. Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2013;26(3):173–178. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

