Baricitinib decreases anti-dsDNA in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: results from a phase II double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 35578304
- PMCID: PMC9109322
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-022-02794-x
Baricitinib decreases anti-dsDNA in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: results from a phase II double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) have substantial unmet medical need. Baricitinib is a Janus kinase (JAK)1 and 2 inhibitor that was shown to have therapeutic benefit in patients with SLE in a phase II clinical trial. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the median change from baseline in conventional serologic biomarkers in subgroups and the overall population of baricitinib-treated patients with SLE, and the SLE Responder Index-4 (SRI-4) response by normalization of anti-dsDNA.
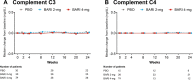
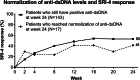
Methods: Data were assessed from the phase II trial I4V-MC-JAHH (NCT02708095). The median change from baseline in anti-dsDNA, IgG, and other conventional serologic markers was evaluated over time in patients who had elevated levels of markers at baseline, and in all patients for IgG. Median change from baseline for baricitinib treatments were compared with placebo. Among patients who were anti-dsDNA positive at baseline, SRI-4 responder rate was compared for those who stayed positive or achieved normal levels by week 24.
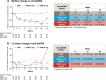
Results: Significant decreases of anti-dsDNA antibodies were observed in response to baricitinib 2 mg and 4 mg compared to placebo beginning at weeks 2 (baricitinib 2 mg = - 14.3 IU/mL, placebo = 0.1 IU/mL) and 4 (baricitinib 4 mg = - 17.9 IU/mL, placebo = 0.02 IU/mL), respectively, continuing through week 24 (baricitinib 2 mg = - 29.6 IU/mL, baricitinib 4 mg = - 15.1 IU/mL, placebo=3.0 IU/mL). Significant reductions from baseline of IgG levels were found for baricitinib 4 mg-treated patients compared to placebo at weeks 12 (baricitinib 4 mg = - 0.65 g/L, placebo = 0.09 g/L) and 24 (baricitinib 4 mg = - 0.60 g/L, placebo = - 0.04 g/L). For patients who were anti-dsDNA positive at baseline, no relationship between achieving SRI-4 responder and normalization of anti-dsDNA was observed by week 24.
Conclusions: Baricitinib treatment resulted in a rapid and sustained significant decrease in anti-dsDNA antibodies compared to placebo among those with positive anti-dsDNA antibodies at baseline, as well as a significant decrease in IgG levels in the 4 mg group at weeks 12 and 24. These data suggest that baricitinib may influence B cell activity in SLE. Further studies are needed to evaluate if reductions in anti-dsDNA levels with baricitinib treatment reflect the impact of baricitinib on B cell activity.
Trial registration: NCT02708095 .
Keywords: Baricitinib; Cytokines; JAK inhibitor; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
TD has received grant support from Chugai, Janssen, Novartis, and Sanofi. He has received consultancy support from AbbVie, Celgene, Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen, Novartis, Roche, Samsung, and UCB, and speaker bureau fees from Eli Lilly and Company and Roche. RFV has received consultancy support from AbbVie, Biotest, BMS, Celgene, Crescendo, Eli Lilly and Company, GSK, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, UCB, and Vertex. AD has received consultancy support from GSK, Eli Lilly and Company, and Celgene and has speaker bureau fees from GSK, Pfizer, Roche, and Janssen. DJW has received consulting support from Amgen, Eli Lilly and Company, EMD Merck Serono, and Pfizer. BJ, JRT, MS, SB, and PF are employees and shareholders of Eli Lilly and Company.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clinical outcomes of baricitinib in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Pooled analysis of SLE-BRAVE-I and SLE-BRAVE-II trials.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 30;20(4):e0320179. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320179. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40305472 Free PMC article.
-
Baricitinib for systemic lupus erythematosus: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial.Lancet. 2018 Jul 21;392(10143):222-231. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31363-1. Lancet. 2018. PMID: 30043749 Clinical Trial.
-
Baricitinib for systemic lupus erythematosus: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial (SLE-BRAVE-II).Lancet. 2023 Mar 25;401(10381):1011-1019. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02546-6. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Lancet. 2023. PMID: 36848919 Clinical Trial.
-
Baricitinib in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 Jun 21;86(8):4738-4744. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002298. eCollection 2024 Aug. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39118746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Baricitinib for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus: a 2019 update.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2019 Jul;15(7):693-700. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2019.1608821. Epub 2019 Apr 25. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30987474 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of baricitinib in the treatment of Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): A Systemic review and meta-analysis.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 21;9(12):e22643. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22643. eCollection 2023 Dec. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38076200 Free PMC article.
-
Lupus Nephritis Risk Factors and Biomarkers: An Update.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 25;24(19):14526. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914526. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37833974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical outcomes of baricitinib in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Pooled analysis of SLE-BRAVE-I and SLE-BRAVE-II trials.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 30;20(4):e0320179. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320179. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40305472 Free PMC article.
-
High serum immunoglobulin D levels in systemic lupus erythematosus: more to be found?Clin Rheumatol. 2023 Apr;42(4):1069-1076. doi: 10.1007/s10067-022-06457-9. Epub 2022 Dec 30. Clin Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36585530
-
The safety and efficacy of Baricitinib for systemic lupus erythematosus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 Sep 5;86(11):6673-6685. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002548. eCollection 2024 Nov. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39525758 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

