Immune Subtype Profiling and Establishment of Prognostic Immune-Related lncRNA Pairs in Human Ovarian Cancer
- PMID: 35578596
- PMCID: PMC9107039
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8338137
Immune Subtype Profiling and Establishment of Prognostic Immune-Related lncRNA Pairs in Human Ovarian Cancer
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Immune Subtype Profiling and Establishment of Prognostic Immune-Related lncRNA Pairs in Human Ovarian Cancer.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jul 12;2023:9758427. doi: 10.1155/2023/9758427. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37475952 Free PMC article.
Abstract
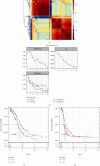
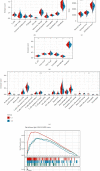
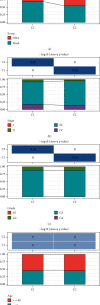
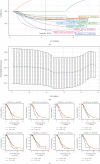
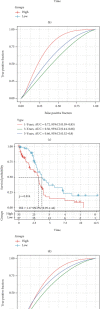
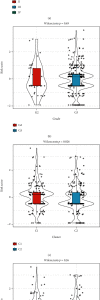
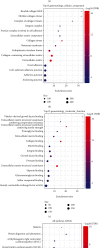
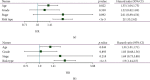
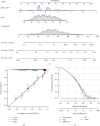
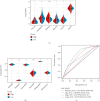
This study collected immune-related genes (IRGs) and used gene expression data from TCGA database to construct a molecular subtype of ovarian cancer (OV) based on immune-related lncRNA gene pairs (IRLnc_GPs). The relationships between molecular subtypes and prognosis and clinical characteristics were further explored. IRGs were acquired from the ImmPort database, and round-robin pairing of immune-related lncRNAs was performed. The NMF algorithm was used to identify molecular subtypes, and the immune score of a single sample was calculated through ESTIMATE, TIMER, ssGSEA, MCPcounter, and CIBERSORT. The relationship between molecular subtypes and immune microenvironments was identified. A hypergeometric test was used to test the lncRNA pairs among the OV molecular subtypes (C1 and C2 subtypes). The BH method was used to screen the different lncRNA pairs, and a predictive risk model was constructed and verified. Finally, correlation analysis between the risk model, immune checkpoint genes, and chemotherapy drugs was carried out. Based on IRLnc_GP to classify 373 OV samples of TCGA, the samples were divided into two subtypes, and the prognosis between the subtypes showed significant differences. The C1 subtype with a poor prognosis was more related to the pathways of tumor occurrence and development. We identified 180 differential lncRNA pairs between subtypes and constructed a prognostic risk model based on 8 IRLnc_GPs. In the independent dataset, the distribution of subtypes in functional modules was different and highly repeatable. There were significant differences in the molecular and clinical characteristics of the subtypes and the drug sensitivity of immunotherapy/chemotherapy. In conclusion, the risk model established based on IRLnc_GP can better evaluate the prognosis of OV samples and can also assess the effects of different drug treatments in the high- and low-risk groups, providing new insights and ideas for the treatment of OV.
Copyright © 2022 Xingling Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Mandilaras V., Garg S., Cabanero M., et al. TP53 mutations in high grade serous ovarian cancer and impact on clinical outcomes: a comparison of next generation sequencing and bioinformatics analyses. International Journal of Gynecological Cancer . 2019;29(2):346–352. doi: 10.1136/ijgc-2018-000087. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

