Social Status and Emotional Competence in Bullying: A Longitudinal Study of the Transition From Kindergarten to Primary School
- PMID: 35578656
- PMCID: PMC9106559
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.817245
Social Status and Emotional Competence in Bullying: A Longitudinal Study of the Transition From Kindergarten to Primary School
Abstract
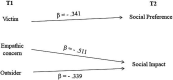
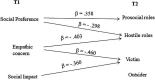
Moving on to a higher level of schooling represents a crucial developmental challenge for children: studies have shown that transitioning to a new school context can increase the perceived importance of peer acceptance, popularity, and adaptation to the new social environment. The aim of this study was to investigate simultaneously the influence of interpersonal variables (social status indices) and personal variables (empathy and understanding of emotions) on role-taking in bullying episodes (hostile, prosocial, victim, and outsider roles) from a longitudinal perspective. These variables were assessed on 41 children in their last year of kindergarten (t1) and in their 1st year of primary school (t2). The main longitudinal results showed that prosocial behaviors are more stable than hostile, victim, and outsider behaviors. Moreover, social preference-together with affective empathy-at t1 had a clear negative predictive effect on hostile roles at t2, while social preference had a positive effect on prosocial roles at t2. Social impact at t1 negatively predicted being a victim at t2. On the other hand, social preference at t2 was negatively predicted only by the victim role at t1. Social impact at t1 had a significant and negative effect on being victimized at t2 while was negatively predicted at t2 by the outsider at t1. Our study-even if exploratory-seems to highlight the existence of a specific, differentiate effect of two distinct social status indices on the participant role-taking in bullying episodes in the transitional period from kindergarten to primary school.
Keywords: bullying; emotional competence; kindergarten; longitudinal approach; primary school; social status.
Copyright © 2022 Farina and Belacchi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any personal, professional, or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Albanese O., Molina P. (2008). Lo sviluppo della comprensione delle emozioni e la sua valutazione. La standardizzazione italiana del Test della Comprensione delle Emozioni (TEC). Unicopli, Milano, I.
-
- Belacchi C. (2008). I ruoli dei partecipanti nel bullismo: una nuova proposta. G. Ital. Psicol. 4, 885–911. doi: 10.1421/28422 - DOI
-
- Boulton M. J., Smith P. K. (1994). Bully/victim problems in middle-school children: stability, self-perceived competence, peer perceptions and peer acceptance. Br. J. Dev. Psychol. 12, 315–329. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-835X.1994.tb00637.x - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources