The state of Medusozoa genomics: current evidence and future challenges
- PMID: 35579552
- PMCID: PMC9112765
- DOI: 10.1093/gigascience/giac036
The state of Medusozoa genomics: current evidence and future challenges
Erratum in
-
Correction to: The state of Medusozoa genomics: current evidence and future challenges.Gigascience. 2022 Dec 12;11:giac115. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giac115. Gigascience. 2022. PMID: 36503974 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
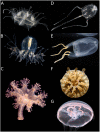
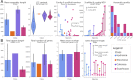
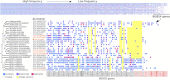
Medusozoa is a widely distributed ancient lineage that harbors one-third of Cnidaria diversity divided into 4 classes. This clade is characterized by the succession of stages and modes of reproduction during metagenic lifecycles, and includes some of the most plastic body plans and life cycles among animals. The characterization of traditional genomic features, such as chromosome numbers and genome sizes, was rather overlooked in Medusozoa and many evolutionary questions still remain unanswered. Modern genomic DNA sequencing in this group started in 2010 with the publication of the Hydra vulgaris genome and has experienced an exponential increase in the past 3 years. Therefore, an update of the state of Medusozoa genomics is warranted. We reviewed different sources of evidence, including cytogenetic records and high-throughput sequencing projects. We focused on 4 main topics that would be relevant for the broad Cnidaria research community: (i) taxonomic coverage of genomic information; (ii) continuity, quality, and completeness of high-throughput sequencing datasets; (iii) overview of the Medusozoa specific research questions approached with genomics; and (iv) the accessibility of data and metadata. We highlight a lack of standardization in genomic projects and their reports, and reinforce a series of recommendations to enhance future collaborative research.
Keywords: annotation; assembly; chromosome number; collaborative genomics; completeness; genome size.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press GigaScience.
Figures

References
-
- World Register of Marine Species . Cnidaria. http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=1267. Accessed 24 November 2021.
-
- Cartwright P, Collins AG. Fossils and phylogenies: integrating multiple lines of evidence to investigate the origin of early major metazoan lineages. Integr Comp Biol. 2007;47(5):744–51. - PubMed
-
- Kayal E, Bentlage B, Pankey MS, et al. . Phylogenomics provides a robust topology of the major cnidarian lineages and insights on the origins of key organismal traits. BMC Evol Biol. 2018;18:68.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

