Chromosomal synapsis defects can trigger oocyte apoptosis without elevating numbers of persistent DNA breaks above wild-type levels
- PMID: 35580048
- PMCID: PMC9177993
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkac355
Chromosomal synapsis defects can trigger oocyte apoptosis without elevating numbers of persistent DNA breaks above wild-type levels
Abstract
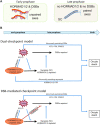
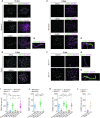
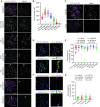
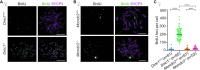
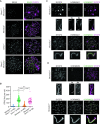
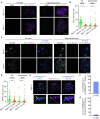
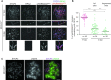
Generation of haploid gametes depends on a modified version of homologous recombination in meiosis. Meiotic recombination is initiated by single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) ends originating from programmed DNA double-stranded breaks (DSBs) that are generated by the topoisomerase-related SPO11 enzyme. Meiotic recombination involves chromosomal synapsis, which enhances recombination-mediated DSB repair, and thus, crucially contributes to genome maintenance in meiocytes. Synapsis defects induce oocyte apoptosis ostensibly due to unrepaired DSBs that persist in asynaptic chromosomes. In mice, SPO11-deficient oocytes feature asynapsis, apoptosis and, surprisingly, numerous foci of the ssDNA-binding recombinase RAD51, indicative of DSBs of unknown origin. Hence, asynapsis is suggested to trigger apoptosis due to inefficient DSB repair even in mutants that lack programmed DSBs. By directly detecting ssDNAs, we discovered that RAD51 is an unreliable marker for DSBs in oocytes. Further, SPO11-deficient oocytes have fewer persistent ssDNAs than wild-type oocytes. These observations suggest that oocyte quality is safeguarded in mammals by a synapsis surveillance mechanism that can operate without persistent ssDNAs.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Repair of exogenous DNA double-strand breaks promotes chromosome synapsis in SPO11-mutant mouse meiocytes, and is altered in the absence of HORMAD1.DNA Repair (Amst). 2018 Mar;63:25-38. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2018.01.007. Epub 2018 Jan 31. DNA Repair (Amst). 2018. PMID: 29414051
-
SPO11-independent DNA repair foci and their role in meiotic silencing.PLoS Genet. 2013 Jun;9(6):e1003538. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003538. Epub 2013 Jun 6. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23754961 Free PMC article.
-
A surge of late-occurring meiotic double-strand breaks rescues synapsis abnormalities in spermatocytes of mice with hypomorphic expression of SPO11.Chromosoma. 2016 Jun;125(2):189-203. doi: 10.1007/s00412-015-0544-7. Epub 2015 Oct 6. Chromosoma. 2016. PMID: 26440409 Free PMC article.
-
DNA double strand break repair, chromosome synapsis and transcriptional silencing in meiosis.Epigenetics. 2010 May 16;5(4):255-66. doi: 10.4161/epi.5.4.11518. Epub 2010 May 16. Epigenetics. 2010. PMID: 20364103 Review.
-
Programmed induction of DNA double strand breaks during meiosis: setting up communication between DNA and the chromosome structure.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013 Apr;23(2):147-55. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2012.12.002. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013. PMID: 23313097 Review.
Cited by
-
BRCA1 safeguards genome integrity by activating chromosome asynapsis checkpoint to eliminate recombination-defective oocytes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 May 7;121(19):e2401386121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2401386121. Epub 2024 May 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38696471 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of the Potential Mechanisms of Follicular Development in Stra8-Deficient Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 15;26(8):3734. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083734. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332359 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Integration of Meiotic Prophase I Progression and Early Oocyte Differentiation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 6:2025.01.06.631470. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.06.631470. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39829852 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Heat shock factor 5 establishes the male germ-line meiotic sex chromosome inactivation through regulation of Smarca4.Heliyon. 2023 Apr 21;9(5):e15194. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15194. eCollection 2023 May. Heliyon. 2023. Retraction in: Heliyon. 2025 Apr 02;11(9):e43282. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e43282. PMID: 37206036 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
A simple immunohistochemical method for perinatal mammalian ovaries revealed different kinetics of oocyte apoptosis caused by DNA damage and asynapsis.Histochem Cell Biol. 2025 Feb 17;163(1):32. doi: 10.1007/s00418-025-02358-5. Histochem Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 39961811
References
-
- Baudat F., Manova K., Yuen J.P., Jasin M., Keeney S.. Chromosome synapsis defects and sexually dimorphic meiotic progression in mice lacking spo11. Mol. Cell. 2000; 6:989–998. - PubMed
-
- Bergerat A., de Massy B., Gadelle D., Varoutas P.C., Nicolas A., Forterre P.. An atypical topoisomerase II from archaea with implications for meiotic recombination. Nature. 1997; 386:414–417. - PubMed
-
- Keeney S., Giroux C.N., Kleckner N.. Meiosis-specific DNA double-strand breaks are catalyzed by spo11, a member of a widely conserved protein family. Cell. 1997; 88:375–384. - PubMed
-
- Robert T., Nore A., Brun C., Maffre C., Crimi B., Bourbon H.M., de Massy B.. The topovib-like protein family is required for meiotic DNA double-strand break formation. Science. 2016; 351:943–949. - PubMed
-
- Romanienko P.J., Camerini-Otero R.D.. The mouse spo11 gene is required for meiotic chromosome synapsis. Mol. Cell. 2000; 6:975–987. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

