ROR1: an orphan becomes apparent
- PMID: 35580162
- PMCID: PMC10653015
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2021014760
ROR1: an orphan becomes apparent
Abstract
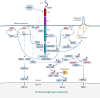
Since its initial identification in 1992 as a possible class 1 cell-surface receptor without a known parent ligand, receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1 (ROR1) has stimulated research, which has made apparent its significance in embryonic development and cancer. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) was the first malignancy found to have distinctive expression of ROR1, which can help distinguish leukemia cells from most noncancer cells. Aside from its potential utility as a diagnostic marker or target for therapy, ROR1 also factors in the pathophysiology of CLL. This review is a report of the studies that have elucidated the expression, biology, and evolving strategies for targeting ROR1 that hold promise for improving the therapy of patients with CLL or other ROR1-expressing malignancies.
© 2022 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: Zilovertamab was developed by T.J.K. and his laboratory and licensed by the University of California to Oncternal+ Therapeutics, Inc, and VelosBio, Inc, which provided stock and research funding.
Figures

References
-
- Masiakowski P, Carroll RD. A novel family of cell surface receptors with tyrosine kinase-like domain. J Biol Chem. 1992;267(36):26181–26190. - PubMed
-
- Oishi I, Takeuchi S, Hashimoto R, et al. Spatio-temporally regulated expression of receptor tyrosine kinases, mRor1, mRor2, during mouse development: implications in development and function of the nervous system. Genes Cells. 1999;4(1):41–56. - PubMed
-
- Matsuda T, Nomi M, Ikeya M, et al. Expression of the receptor tyrosine kinase genes, Ror1 and Ror2, during mouse development. Mech Dev. 2001;105(1-2):153–156. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez-Niedenführ M, Pröls F, Christ B. Expression and regulation of ROR-1 during early avian limb development. Anat Embryol (Berl) 2004;207(6):495–502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

