Unsaturation in the Fatty Acids of Phospholipids Drastically Alters the Structure and Toxicity of Insulin Aggregates Grown in Their Presence
- PMID: 35580189
- PMCID: PMC9170185
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.2c00559
Unsaturation in the Fatty Acids of Phospholipids Drastically Alters the Structure and Toxicity of Insulin Aggregates Grown in Their Presence
Abstract
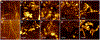
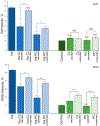
Lipid bilayers play an important role in the pathological assembly of amyloidogenic proteins and peptides. This assembly yields oligomers and fibrils, which are highly toxic protein aggregates. In this study, we investigated the role of saturation in fatty acids of two phospholipids that are present in cell membranes. We found that unsaturated cardiolipin (CL) drastically shortened the lag phase of insulin aggregation. Furthermore, structurally and morphologically different aggregates were formed in the presence of unsaturated CL vs saturated CL. These aggregates exerted drastically different cell toxicity. Both saturated and unsaturated phosphatidylcholine (PC) were able to inhibit insulin aggregation equally efficiently. Similar to CL, structurally different aggregates were formed in the presence of saturated and unsaturated PC. These aggregates exerted different cell toxicities. These results show that unsaturated phospholipids catalyze the formation of more toxic amyloid aggregates comparing to those formed in the presence of saturated lipids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
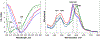

References
-
- Fitzner D; Bader JM; Penkert H; Bergner CG; Su M; Weil MT; Surma MA; Mann M; Klose C; Simons M Cell-Type- and Brain-Region-Resolved Mouse Brain Lipidome. Cell Rep 2020, 32, 108132. - PubMed
-
- Pope S; Land JM; Heales SJ Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Neurodegeneration; Cardiolipin a Critical Target? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1777, 794–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

