AENEAS: A Randomized Phase III Trial of Aumolertinib Versus Gefitinib as First-Line Therapy for Locally Advanced or MetastaticNon-Small-Cell Lung Cancer With EGFR Exon 19 Deletion or L858R Mutations
- PMID: 35580297
- PMCID: PMC9509093
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.21.02641
AENEAS: A Randomized Phase III Trial of Aumolertinib Versus Gefitinib as First-Line Therapy for Locally Advanced or MetastaticNon-Small-Cell Lung Cancer With EGFR Exon 19 Deletion or L858R Mutations
Abstract
Purpose: Aumolertinib (formerly almonertinib; HS-10296) is a novel third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor approved in China. This double-blind phase III trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of aumolertinib compared with gefitinib as a first-line treatment for locally advanced or metastatic EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC; ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03849768).
Methods: Patients at 53 sites in China were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive either aumolertinib (110 mg) or gefitinib (250 mg) once daily. The primary end point was progression-free survival (PFS) per investigator assessment.
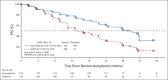
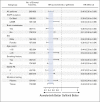
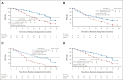
Results: A total of 429 patients who were naïve to treatment for locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC were enrolled. PFS was significantly longer with aumolertinib compared with gefitinib (hazard ratio, 0.46; 95% CI, 0.36 to 0.60; P < .0001). The median PFS with aumolertinib was 19.3 months (95% CI, 17.8 to 20.8) versus 9.9 months with gefitinib (95% CI, 8.3 to 12.6). Objective response rate and disease control rate were similar in the aumolertinib and gefitinib groups (objective response rate, 73.8% and 72.1%, respectively; disease control rate, 93.0% and 96.7%, respectively). The median duration of response was 18.1 months (95% CI, 15.2 to not applicable) with aumolertinib versus 8.3 months (95% CI, 6.9 to 11.1) with gefitinib. Adverse events of grade ≥ 3 severity (any cause) were observed in 36.4% and 35.8% of patients in the aumolertinib and gefitinib groups, respectively. Rash and diarrhea (any grade) were observed in 23.4% and 16.4% of patients who received aumolertinib compared with 41.4% and 35.8% of those who received gefitinib, respectively.
Conclusion: Aumolertinib is a well-tolerated third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor that could serve as a treatment option for EGFR-mutant NSCLC in the first-line setting.
Conflict of interest statement
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures
Comment in
-
Aumolertinib in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer: Will the Promise of Cost Disruption Ease Access?J Clin Oncol. 2022 Sep 20;40(27):3103-3105. doi: 10.1200/JCO.22.00903. Epub 2022 Jun 9. J Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35679530 No abstract available.
References
-
- Goss G, Tsai CM, Shepherd FA, et al. : Osimertinib for pretreated EGFR Thr790Met-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (AURA2): A multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol 17:1643-1652, 2016 - PubMed
-
- Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, et al. : Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 378:113-125, 2018 - PubMed
-
- Ramalingam SS, Vansteenkiste J, Planchard D, et al. : Overall survival with osimertinib in untreated, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N Engl J Med 382:41-50, 2020 - PubMed
-
- Bao R, Zhang F, Tong Z, et al. : Discovery of a third-generation EGFR inhibitor, which is highly selective and potent against both resistant and activating EGFR mutations for NSCLC therapy. Cancer Res 76, 2016. (suppl; abstr 3036)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

