Real-world use of tisagenlecleucel in infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 35580324
- PMCID: PMC9327536
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021006393
Real-world use of tisagenlecleucel in infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
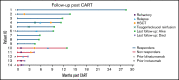
Infants with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) have poor outcomes because of chemotherapy resistance leading to high relapse rates. Tisagenlecleucel, a CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CART) therapy, is US Food and Drug Administration approved for relapsed or refractory B-ALL in patients ≤25 years; however, the safety and efficacy of this therapy in young patients is largely unknown because children <3 years of age were excluded from licensing studies. We retrospectively evaluated data from the Pediatric Real-World CAR Consortium to examine outcomes of patients with infant B-ALL who received tisagenlecleucel between 2017 and 2020 (n = 14). Sixty-four percent of patients (n = 9) achieved minimal residual disease-negative remission after CART and 50% of patients remain in remission at last follow-up. All patients with high disease burden at time of CART infusion (>M1 marrow) were refractory to this therapy (n = 5). Overall, tisagenlecleucel was tolerable in this population, with only 3 patients experiencing ≥grade 3 cytokine release syndrome. No neurotoxicity was reported. This is the largest report of tisagenlecleucel use in infant B-ALL and shows that this therapy is safe and can be effective in this population. Incorporating this novel immunotherapy into the treatment of infant B-ALL offers a promising therapy for a highly aggressive leukemia.
Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Guest EM, Stam RW. Updates in the biology and therapy for infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2017;29(1):20-26. - PubMed
-
- Pieters R, Schrappe M, De Lorenzo P, et al. . A treatment protocol for infants younger than 1 year with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (Interfant-99): an observational study and a multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2007;370(9583):240-250. - PubMed
-
- Pieters R, De Lorenzo P, Ancliffe P, et al. . Outcome of infants younger than 1 year with acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated with the Interfant-06 protocol: results from an international phase III randomized study. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37(25):2246-2256. - PubMed
-
- Driessen EM, de Lorenzo P, Campbell M, et al. . Outcome of relapsed infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated on the interfant-99 protocol [published correction appears in Leukemia. 2017;31(12):2854]. Leukemia. 2016;30(5):1184-1187. - PubMed
-
- Brown PA, Kairalla JA, Hilden JM, et al. . FLT3 inhibitor lestaurtinib plus chemotherapy for newly diagnosed KMT2A-rearranged infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Children’s Oncology Group trial AALL0631 [published correction appears in Leukemia. 2021;35(5):1527]. Leukemia. 2021;35(5):1279-1290. - PMC - PubMed