Giant retroperitoneal well-differentiated liposarcoma presenting in emergency with intestinal occlusion: Case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 35580411
- PMCID: PMC9117537
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2022.107152
Giant retroperitoneal well-differentiated liposarcoma presenting in emergency with intestinal occlusion: Case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Introduction and importance: Liposarcoma (LPS) represents the most common type of retroperitoneal sarcoma (RPS) and can be classified into four subtypes. Preoperative diagnosis of retroperitoneal liposarcoma (RLPS) is a challenge because of its late and nonspecific clinical presentation. Imaging may be helpful for determining the correct diagnosis. Surgery represents a potentially curative treatment of RLPS.
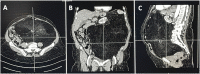
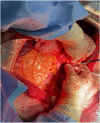
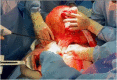
Case presentation: A 55-year-old Caucasian female presented to the Emergency Department with a two-day history of abdominal pain, abdominal distension, inability to pass gas or stool, nausea, vomiting and lipothymia. Abdominal examination revealed abdominal distention, abdominal pain without obvious muscle guarding and a giant non-tender mass. Laboratory tests reported neutrophilic leukocytosis and anemia. Abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) showed a heterogeneous and hypodense giant retroperitoneal mass compressing and displacing the surrounding organs and vessels. The patient underwent excision of a giant retroperitoneal mass. The postoperative course of the patient was uneventful.
Clinical discussion: RLPS is a malignant neoplasm that can slowly grow to enormous size with possible involvement of adjacent organs and vessels; it may recur locally and has a minimal capacity to metastasize. Preoperative diagnosis and staging of RLPS are important to establish appropriate management and prognosis. Surgery represents the gold standard for non-metastatic RLPS treatment.
Conclusion: RLPS is a rare malignant neoplasm generally difficult to detect early due to its late and nonspecific clinical presentation. CECT represents the most commonly used modality for diagnosis, staging and preoperative evaluation. Surgery represents the appropriate treatment of non-metastatic RLPS.
Keywords: Case report; Liposarcoma; Retroperitoneal; Sarcoma; Surgery; Well-differentiated.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors certify that there is no conflict of interest regarding the material discussed in the manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Idiopathic giant pancreatic pseudocyst presenting in emergency with abdominal compartment syndrome and intestinal occlusion: Case report and review of the literature.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021 Apr;81:105812. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2021.105812. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 33887838 Free PMC article.
-
Giant retroperitoneal liposarcoma treated with radical conservative surgery: A case report and review of literature.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Jul 6;10(19):6636-6646. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i19.6636. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 35979304 Free PMC article.
-
Giant retroperitoneal liposarcoma: A case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2022 Aug;97:107465. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2022.107465. Epub 2022 Jul 30. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35917605 Free PMC article.
-
Retroperitoneal sarcomas: from diagnosis to treatment. Case series and review of the literature.G Chir. 2020 Jan-Feb;41(1):18-33. G Chir. 2020. PMID: 32038009 Review.
-
Giant retroperitoneal sarcoma: a case report and review of the management of retroperitoneal sarcomas.Am Surg. 2002 Jan;68(1):52-6. Am Surg. 2002. PMID: 12467318 Review.
Cited by
-
Giant retroperitoneal liposarcoma with multiple organ involvement: a case report and literature review.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Aug 29;25(1):281. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03701-z. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39210338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dark Topics on Giant Retroperitoneal Liposarcoma: A Systematic Review of 157 Cases.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Feb 21;17(5):740. doi: 10.3390/cancers17050740. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40075588 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

