Association between somatosensory sensitivity and regional gray matter volume in healthy young volunteers: a voxel-based morphometry study
- PMID: 35580840
- PMCID: PMC9977372
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhac188
Association between somatosensory sensitivity and regional gray matter volume in healthy young volunteers: a voxel-based morphometry study
Abstract
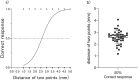
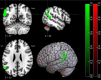
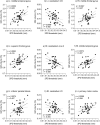
Two-point discrimination (2PD) test reflects somatosensory spatial discrimination ability, but evidence on the relationship between 2PD and cortical gray matter (GM) volume is limited. This study aimed to analyze the relationship between cortical GM volume and 2PD threshold in young healthy individuals and to clarify the characteristics of brain structure reflecting the individual differences in somatosensory function. 2PD was measured in 42 healthy (20 females) volunteers aged 20-32 years using a custom-made test system that can be controlled by a personal computer. The 2PD of the right index finger measured with this device has been confirmed to show good reproducibility. T1-weighted images were acquired using a 3-T magnetic resonance imaging scanner for voxel-based morphometry analysis. The mean 2PD threshold was 2.58 ± 0.54 mm. Whole-brain multiple regression analysis of the relationship between 2PD and GM volume showed that a lower 2PD threshold (i.e. better somatosensory function) significantly correlated with decreased GM volume from the middle temporal gyrus to the inferior parietal lobule (IPL) in the contralateral hemisphere. In conclusion, a lower GM volume in the middle temporal gyrus and IPL correlates with better somatosensory function. Thus, cortical GM volume may be a biomarker of somatosensory function.
Keywords: 2-point discrimination; VBM; gray matter; inferior parietal lobe; middle temporal gyrus.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permission@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Akatsuka K, Noguchi Y, Harada T, Sadato N, Kakigi R. Neural codes for somatosensory two-point discrimination in inferior parietal lobule: an fMRI study. NeuroImage. 2008:40:852–858. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J. A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage. 2007:38:95–113. - PubMed
-
- Bermudez P, Lerch JP, Evans AC, Zatorre RJ. Neuroanatomical correlates of musicianship as revealed by cortical thickness and voxel-based morphometry. Cereb Cortex. 2009:19:1583–1596. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

