Identification of combined biomarkers for predicting the risk of osteoporosis using machine learning
- PMID: 35580864
- PMCID: PMC9186773
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.204084
Identification of combined biomarkers for predicting the risk of osteoporosis using machine learning
Abstract
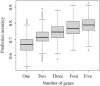
Osteoporosis is a severe chronic skeletal disorder that affects older individuals, especially postmenopausal women. However, molecular biomarkers for predicting the risk of osteoporosis are not well characterized. The aim of this study was to identify combined biomarkers for predicting the risk of osteoporosis using machine learning methods. We merged three publicly available gene expression datasets (GSE56815, GSE13850, and GSE2208) to obtain expression data for 6354 unique genes in postmenopausal women (45 with high bone mineral density and 45 with low bone mineral density). All machine learning methods were implemented in R, with the GEOquery and limma packages, for dataset download and differentially expressed gene identification, and a nomogram for predicting the risk of osteoporosis was constructed. We detected 378 significant differentially expressed genes using the limma package, representing 15 major biological pathways. The performance of the predictive models based on combined biomarkers (two or three genes) was superior to that of models based on a single gene. The best predictive gene set among two-gene sets included PLA2G2A and WRAP73. The best predictive gene set among three-gene sets included LPN1, PFDN6, and DOHH. Overall, we demonstrated the advantages of using combined versus single biomarkers for predicting the risk of osteoporosis. Further, the predictive nomogram constructed using combined biomarkers could be used by clinicians to identify high-risk individuals and in the design of efficient clinical trials to reduce the incidence of osteoporosis.
Keywords: combined biomarker; gene expression; machine learning; osteoporosis; risk prediction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Billington EO, Leslie WD, Brown JP, Prior JC, Morin SN, Kovacs CS, Kaiser SM, Lentle BC, Anastassiades T, Towheed T, Kline GA. Simulated effects of early menopausal bone mineral density preservation on long-term fracture risk: a feasibility study. Osteoporos Int. 2021; 32:1313–20. 10.1007/s00198-021-05826-5 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

