Delayed drug hypersensitivity reaction to secukinumab in a patient with hidradenitis suppurativa
- PMID: 35580946
- PMCID: PMC9114844
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2022-249684
Delayed drug hypersensitivity reaction to secukinumab in a patient with hidradenitis suppurativa
Abstract
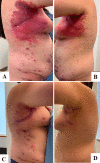
A woman in her 30s presented to the dermatology clinic with widespread, pruritic, red papules and plaques involving the ears, trunk and extremities. The rash developed a few days after receiving her second injection of secukinumab, which was initiated for recalcitrant Hurley stage III hidradenitis suppurativa. Investigations revealed a psoriasiform drug hypersensitivity reaction secondary to secukinumab. In this report, we describe the clinical course, histopathological correlation and treatment of this rarely documented reaction.
Keywords: Dermatology; Hidradenitis suppurativa; Skin; Unwanted effects / adverse reactions.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2022. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
