Purification, characterization, and determination of biological activities of water-soluble polysaccharides from Mahonia bealei
- PMID: 35581215
- PMCID: PMC9114413
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-11661-3
Purification, characterization, and determination of biological activities of water-soluble polysaccharides from Mahonia bealei
Abstract
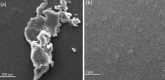
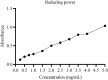
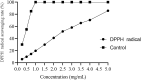
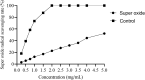
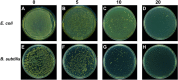
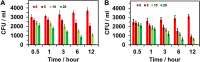
Mahonia bealei is one of the important members of the genus Mahonia and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). Several compounds isolated from this plant have exhibited useful biological activities. Polysaccharides, an important biomacromolecule have been underexplored in case of M. bealei. In this study, hot water extraction and ethanol precipitation were used for the extraction of polysaccharides from the stem of M. bealei, and then extract was purified using ultrafiltration membrane at 50,000 Da cut off value. Characterization of the purified M. bealei polysaccharide (MBP) was performed using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR), along with Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), X-ray crystallography XRD analysis and Thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA). The purified polysaccharide MBP was tested for antioxidant potential by determining its reducing power, besides determining the DPPH, ABTS, superoxide radical, and hydroxyl radical scavenging along with ferrous ion chelating activities. An increased antioxidant activity of the polysaccharide was reported with increase in concentration (0.5 to 5 mg/ml) for all the parameters. Antimicrobial potential was determined against gram positive and gram-negative bacteria. 20 µg/ml MBP was found appropriate with 12 h incubation period against Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis bacteria. We conclude that polysaccharides from M. bealei possess potential ability of biological importance; however, more studies are required for elucidation of their structure and useful activities.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Zhang, H. et al.Additions to the Cycadaceous flora of China. (Actaentiarum Naturalism Universitatis Sunyatseni, 1998).
-
- Loconte H. Berberidaceae. Flowering Plants·Dicotyledons. Springer; 1993. pp. 147–152.
-
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China 2010. (China Medical Science Press, Beijing, China, 2010).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

