Complete response to combination therapy using nivolumab and ipilimumab for metastatic, sarcomatoid collecting duct carcinoma presenting with high expression of programmed death-ligand 1: a case report
- PMID: 35581611
- PMCID: PMC9116048
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-022-03426-3
Complete response to combination therapy using nivolumab and ipilimumab for metastatic, sarcomatoid collecting duct carcinoma presenting with high expression of programmed death-ligand 1: a case report
Abstract
Background: Collecting duct carcinoma and sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma are tumors with poor prognosis. Immune checkpoint inhibitors have been established as the standard treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma. Some cases of remission of collecting duct carcinoma and sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma have been reported using immune checkpoint inhibitor interventions. Specifically, sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma expresses high levels of programmed death-ligand 1, an immune checkpoint protein, and immune checkpoint inhibitors have been reported to be highly effective for treating sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma.
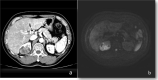
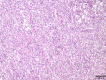
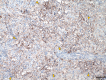
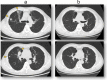
Case presentation: We describe the case of a 70-year-old Japanese male who underwent radical right nephrectomy for a right renal mass identified on computed tomography. The pathological examination demonstrated that the renal mass was urothelial carcinoma and collecting duct carcinoma with sarcomatoid changes, and programmed death-ligand 1 was highly expressed with a tumor proportion score of more than 10%. There was no evident submucosal connective tissue invasion in the urothelial carcinoma component, and collecting duct carcinoma was diagnosed as primary cancer. The tumor-node-metastasis classification was pT3aN0, venous invasion 1, lymphovascular invasion 0, and Fuhrman nuclear grade 4. Two months after the nephrectomy, multiple metastases were observed in both lungs, the right hilar lymph node, and the S6 segment of the right liver lobe. We initiated first-line combination therapy with nivolumab (240 mg, fixed dose) and ipilimumab (1 mg/kg). One day after administration, the patient developed drug-induced interstitial pneumonia, thus we applied steroid injections. After one administration of immunotherapy, the metastatic lesion showed complete response within 6 months, which was maintained after 3 years.
Conclusion: We report the first case of complete response to a single dose of combination therapy with nivolumab and ipilimumab for metastatic collecting duct carcinoma with sarcomatoid changes and high expression of programmed death-ligand 1. This case suggests high expectations for immune checkpoint inhibitors as treatment for sarcomatoid-transformed renal carcinoma tumors that express high levels of programmed death-ligand 1.
Keywords: Case report; Collecting duct carcinoma; Immune checkpoint inhibitors; Immune-related adverse events; Programmed death-ligand 1; Sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Srigley JR, Eble JN. Collecting duct carcinoma of kidney. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1998;15(1):54–67. - PubMed
-
- Mimura A, Sakuma T, Furuta M, Tanigawa N, Takamizu R, Kawano K. Sarcomatoid collecting duct carcinoma of kidney diagnosed with urine and renal pelvic lavage cytology. Diagn Cytopathol. 2010;38(8):603–606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

