Glucagon-like peptide-1 attenuates diabetes-associated osteoporosis in ZDF rat, possibly through the RAGE pathway
- PMID: 35581617
- PMCID: PMC9112483
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-022-05396-5
Glucagon-like peptide-1 attenuates diabetes-associated osteoporosis in ZDF rat, possibly through the RAGE pathway
Abstract
Background: Diabetes-associated osteoporosis are partly caused by accumulation of advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs). Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) has been shown to regulate bone turnover. Here we explore whether GLP-1 receptor agonist (GLP1RA) can have a beneficial effect on bone in diabetes by ameliorating AGEs.
Methods: In the present study, we evaluated the effects of the GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide, insulin and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor saxagliptin on Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Meanwhile, we observed the effect of GLP-1 on AGEs-mediated osteoblast proliferation and differentiation and the signal pathway.
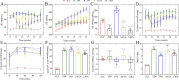
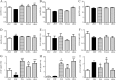
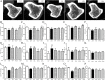
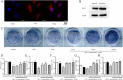
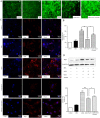
Results: Liraglutide prevented the deterioration of trabecular microarchitecture and enhanced bone strength. Moreover, it increased serum Alpl, Ocn and P1NP levels and decreased serum CTX. In vitro we confirmed that GLP-1 could attenuate AGEs-mediated damage in osteogenic proliferation and differentiation. Besides, GLP-1 down-regulated the ROS that caused by AGEs and the mRNA and protein expression of Rage .
Conclusions: Altogether, our findings suggest that GLP-1 receptor agonist promotes osteoblastogenesis and suppresses bone resorption on obese type 2 diabetic rats to a certain degree. The mechanism of these effects may be partly mediated by AGEs-RAGE-ROS pathway via the interaction with GLP-1 receptor.
Keywords: Advanced glycation endproducts; Diabetes; Glucagon-like peptide-1; Liraglutide; Osteoporosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

