Structural and functional specificity of H3K36 methylation
- PMID: 35581654
- PMCID: PMC9116022
- DOI: 10.1186/s13072-022-00446-7
Structural and functional specificity of H3K36 methylation
Abstract
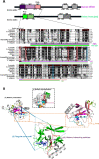
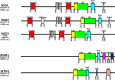
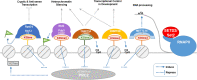
The methylation of histone H3 at lysine 36 (H3K36me) is essential for maintaining genomic stability. Indeed, this methylation mark is essential for proper transcription, recombination, and DNA damage response. Loss- and gain-of-function mutations in H3K36 methyltransferases are closely linked to human developmental disorders and various cancers. Structural analyses suggest that nucleosomal components such as the linker DNA and a hydrophobic patch constituted by histone H2A and H3 are likely determinants of H3K36 methylation in addition to the histone H3 tail, which encompasses H3K36 and the catalytic SET domain. Interaction of H3K36 methyltransferases with the nucleosome collaborates with regulation of their auto-inhibitory changes fine-tunes the precision of H3K36me in mediating dimethylation by NSD2 and NSD3 as well as trimethylation by Set2/SETD2. The identification of specific structural features and various cis-acting factors that bind to different forms of H3K36me, particularly the di-(H3K36me2) and tri-(H3K36me3) methylated forms of H3K36, have highlighted the intricacy of H3K36me functional significance. Here, we consolidate these findings and offer structural insight to the regulation of H3K36me2 to H3K36me3 conversion. We also discuss the mechanisms that underlie the cooperation between H3K36me and other chromatin modifications (in particular, H3K27me3, H3 acetylation, DNA methylation and N6-methyladenosine in RNAs) in the physiological regulation of the epigenomic functions of chromatin.
Keywords: ASH1L; H3K36; Methylation; NSD2; NSD3; SETD2; Set2.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

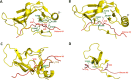
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

